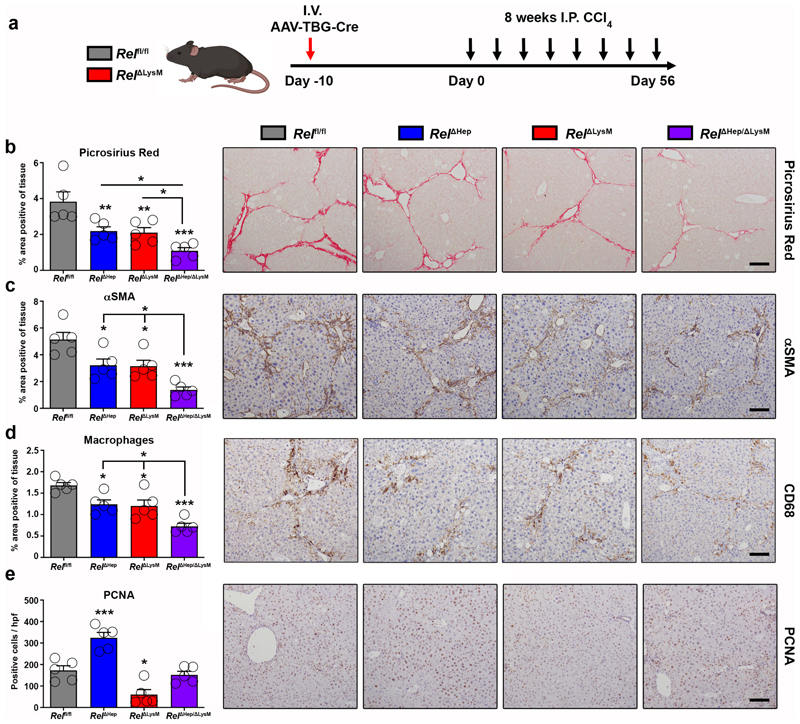
Figure 6. Figure 6. Epithelial and macrophage c-Rel signalling synergistically promote hepatic fibrosis but antagonistically regulate hepatic regeneration in mice.
(a) Schematic shows the timeline of intravenous injection administration of adeno-associated virus expressing Cre recombinase (AAV-TBG-Cre) to Rel flfl or RelΔLysM mice to create RelΔHep and RelΔHep/ΔLysM prior to chronic CCl4 injury. (b) Histological quantification and representative images of Picrosirius red stained sections from chronic CCl4 injured Rel flfl, RelΔHep (p value = 0.0093), RelΔLysM (p value = 0.0074) and RelΔHep/ΔLysM (p value = 0.0001) mice. (c) Histological quantification and representative images of αSMA stained sections from chronic CCl4 injured Rel flfl, RelΔHep (p value = 0.028), RelΔLysM (p value = 0.023) and RelΔHep/ΔLysM (p value = 0.0001) mice. (d) Histological quantification and representative images of CD68 (macrophages) sections from chronic CCl4 injured Rel flfl, RelΔHep(p value = 0.0316), RelΔLysM (p value = 0.0181) and RelΔHep/ΔLysM (p value = 0.00012) mice. (e) Histological quantification and representative images of PCNA stained sections from chronic CCl4 injured Rel flfl, RelΔHep (p value = 0.0008), RelΔLysM (p value = 0.0106) and RelΔHep/ΔLysM mice. Data are mean ± s.e.m. in 5 mice/group. Scale bars equal 100 microns. All P values were calculated using a one-way ANOVA with Tukey post-hoc t-test (* P <0.05, ** P <0.01, *** P <0.001).