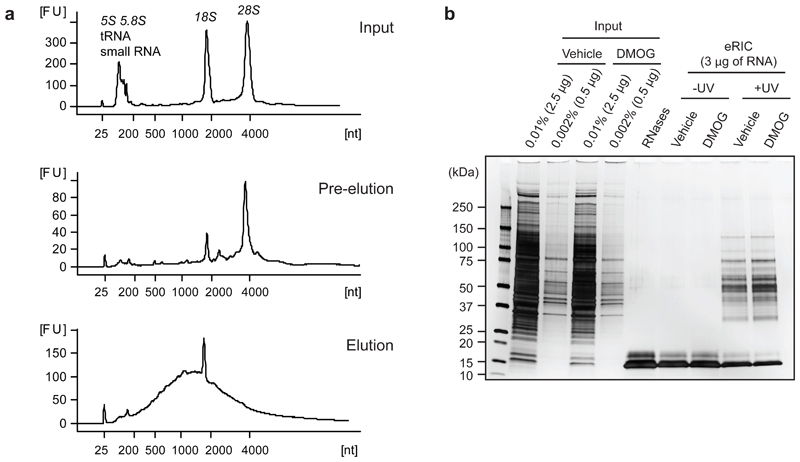
Figure 4. eRIC quality controls.
Poly(A) RNA and associated RBPs were purified from proliferating human leukemia cells (Jurkat) with eRIC and analyzed as follows.a) Representative bioanalyzer profiles of RNA extracted from input material (top), eRIC pre-eluates (middle), and eRIC heat-eluted samples (bottom). rRNAs, tRNAs and small RNAs are predominant in inputs and still present in pre-eluates. eRIC heat-eluted samples display a strong enrichment of RNA species with a size range characteristic of mRNAs. Both 28S rRNA and the small RNAs are undetectable in the heat eluates, although a residual amount of 18S rRNA is consistently observed. [FU] fluorescent units, [nt] length of RNA in number of nucleotides.b) eRIC was performed on Jurkat cells incubated for 6 h with 0.5 mM of the a-ketoglutarate antagonist dimethyloxalylglycine (DMOG) or vehicle (DMSO). Aliquots of the RNase-eluted samples and inputs were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and silver staining. Except for the RNase A and T1 bands (~15 KDa), proteins are only detected in eRIC eluates if cells were UV-irradiated. Protein patterns in untreated and DMOG-treated samples are virtually indistinguishable, which agrees with the proteomic results that revealed a very limited RBP pool (61 proteins out of 721) responding to DMOG14.