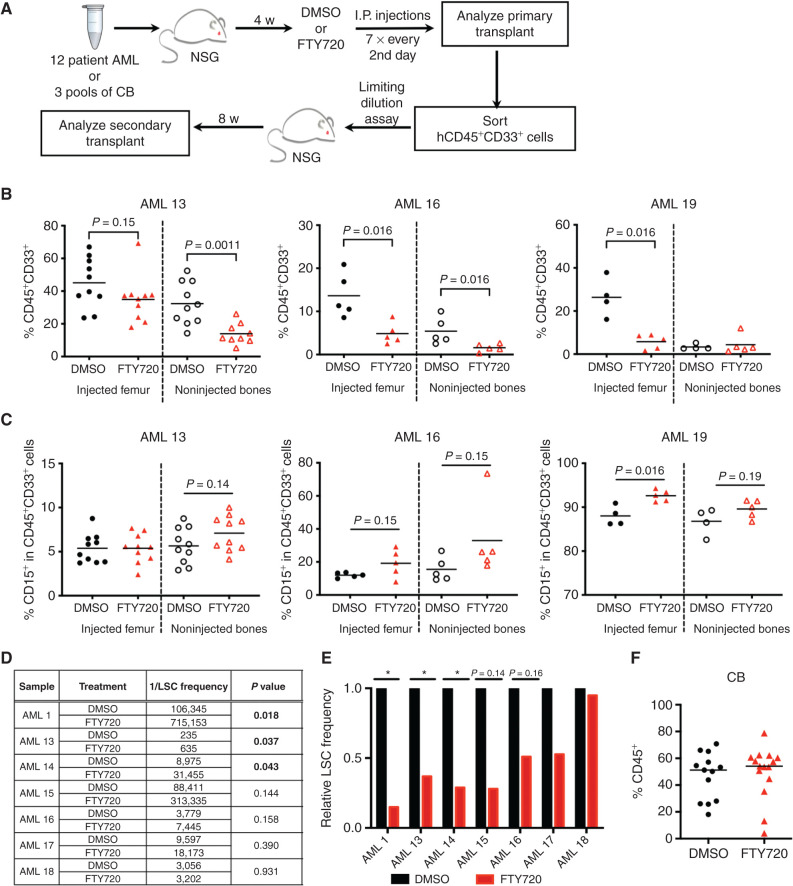
Figure 7.
S1P signaling modulation in vivo targets LSC function in human AML. A–F, Preclinical targeting of the sphingolipid pathway with the S1P prodrug FTY720, clinically known as fingolimod, in samples of patients with AML or CB (n = 3) in vivo. A, Experimental schematic for xenotransplantation. AMLs with >20% engraftment in the injected femur and/or that showed decrease in AML burden were taken through secondary transplant to enumerate LSC frequency in D. B, AML engraftment for each mouse of the three FTY720 (red) responders relative to DMSO control (black), as defined by significant decrease of AML burden at 6 weeks after transplant. AML 13 is a treatment-resistant sample, AML 16 is a relapse sample, and AML 19 is a diagnosis sample. Significance calculated by Mann–Whitney test. See Supplementary Fig. S10 for additional engraftment data. C, Percentage of CD15+ cells in the indicated xenografts. D and E, LSC frequency for indicated AMLs was determined in limiting dilution serial transplantation assays and calculated with ELDA. Mice were considered engrafters if CD45+CD33+ cells >0.5%. The calculated LSC frequency and P value for FTY720 samples relative to DMSO control samples are shown in D, and the relative secondary LSC frequency is shown in E. F, Human CD45+ engraftment of CB following treatment with DMSO or FTY720 at 6 weeks after transplantation.