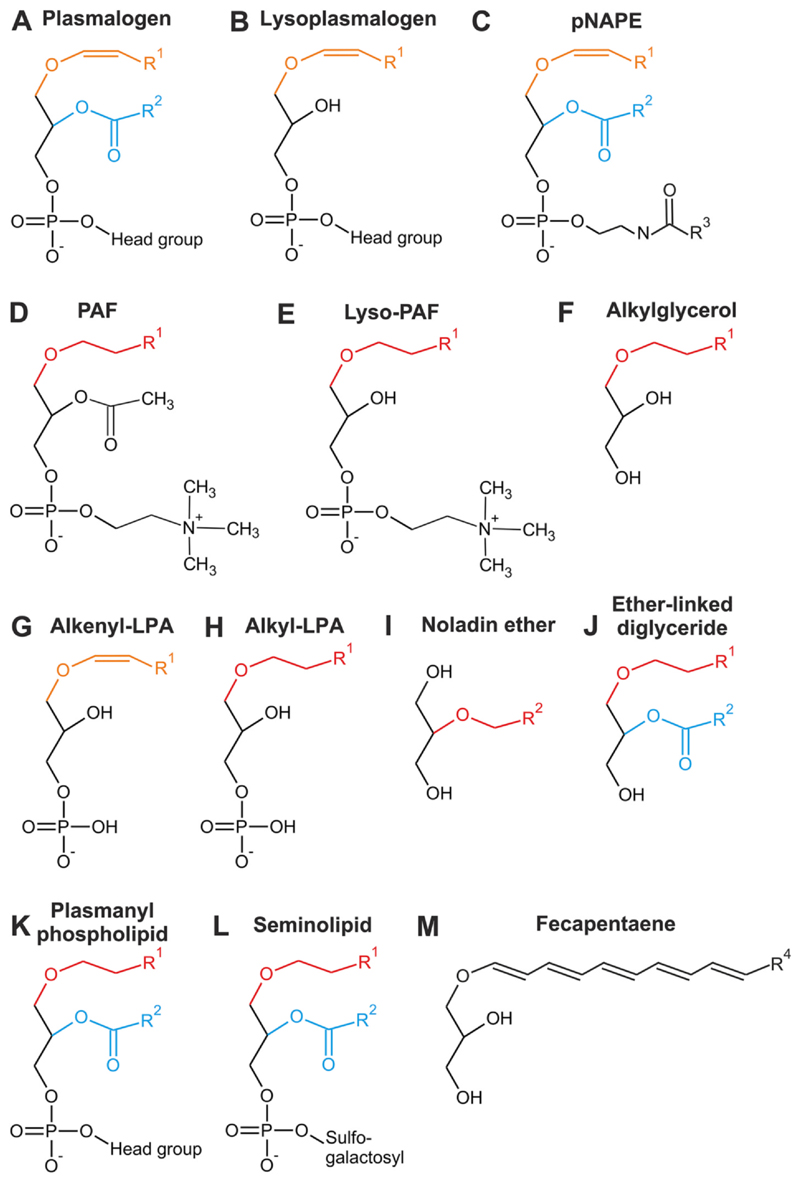
Fig. 2. Structure of ether lipids with reported involvement in signaling processes.
A prototypic plasmalogen (A), lysoplasmalogen (B), N-acyl ethanolamine plasmalogen (pNAPE; C), platelet-activating factor (PAF; D), lyso-PAF (E), alkyl- glycerol (F), alkenyl-lysophosphatidic acid (alkenyl- LPA; G), alkyl-LPA (H), noladin ether (I), ether- linked diglyceride (J), plasmanyl phospholipid (K), seminolipid (L) and fecapentaene (M) are shown with alkyl groups (ether-bonded) colored red, al-kenyl groups (vinyl ether-bonded) orange and acyl groups (ester-bonded) blue. Head groups in (A), (B) and (J) are predominantly ethanolamine or choline. R1 represents alkyl residues originating from primary alcohols synthesized by FAR (mainly C16:0, C18:1 or C18:0 but also other, less common species have been reported). R2 and R3 designate a wider range of saturated and unsaturated fatty acyl chains. In plasmalogens (A), R2 is usually a PUFA residue; in the case of noladin ether (H), R2 indicates the ether- bonded arachidonyl moiety. R4 constitutes C2H5 (fecapentaene-12) or C4H9 (fecapentaene-14).