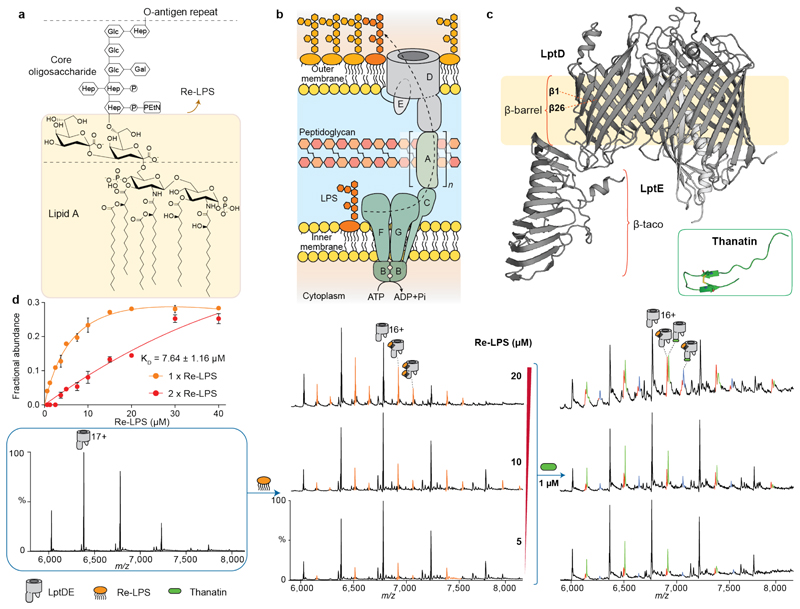
Figure 1. Schematic of the LPS transport system and nMS analysis of LptDE, Re-LPS and thanatin.
(a) Molecular structure of LPS: lipid A portion, core oligosaccharide and the O-antigen repeat, consisting of a high MW polysaccharide with multiple branching. Re-LPS is a substructure of LPS consisting of lipid A bound to two Kdo moieties. (b) Schematic of the Lpt system: LPS is transported from the inner membrane (IM) to the outer membrane (OM) through a multiprotein complex comprising seven proteins. LPS is extracted from the IM via the ABC transporter LptB2FG interacting with the single transmembrane protein LptC. LptA forms a head-to-tail oligomer across the periplasm interacting with LptC on the N-terminus and LptD on the C-terminus. LPS is then inserted in the outer leaflet of the OM by the heterodimer LptDE. (c) X-ray crystal structure of the OM plug-and-barrel complex LptDE (PDB ID: 5IV9). LptD presents a β-barrel transmembrane region and a β-taco soluble region that contributes to the formation of the periplasmic bridge. LptE is a lipoprotein inserted into the larger lobe formed of the LptD β-barrel. Inset: 3D-structure of thanatin (PDB ID: 5XO4). (d) nMS analysis of LptDE ligand binding. LptDE (5μM, left) in 0.5% C8E4 was incubated with increasing concentrations of Re-LPS (centre, orange peaks), allowing for the calculation of an apparent KD for the first binding event, as described in the methods section. Error bars represent s.d. (n = 3). In a further experiment, Re-LPS-bound LptDE was supplemented with 1 μM thanatin (right). New charge state series corresponding to LptDE bound to thanatin (green) and both Re-LPS and thanatin (purple) are observed. Detailed information on theoretical and experimental molecular masses is provided in Supplementary Table 1.