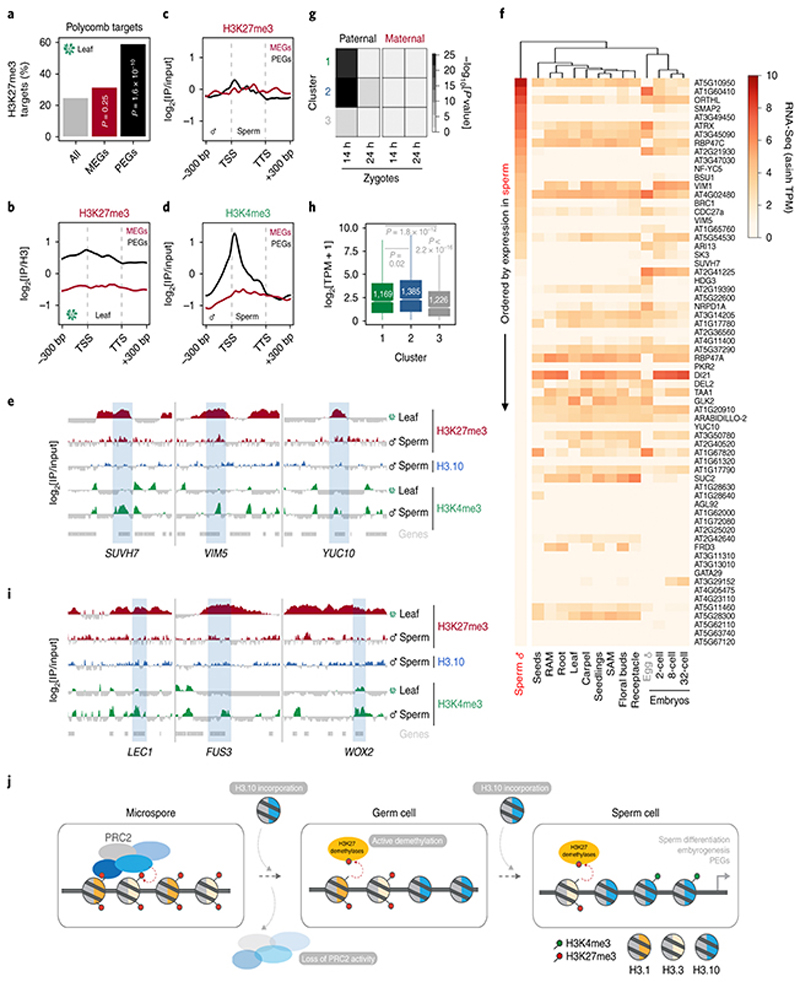
Fig. 5. Sperm chromatin state forecasts gene expression in the next generation.
a, Percentage of MEGs (n = 57 genes) and PEGs (n = 66 genes) overlapping with somatic H3K27me3 domains. Significance was determined by chi-square analysis compared to proportion in Arabidopsis (n = 28,775 genes). b-c, H3K27me3 signal over MEGs and PEGs in leaves (b) and sperm (c). d, H3K4me3 signal over MEGs and PEGs in sperm. Plotted in c,d is the ChIP-seq log2 enrichment relative to input; b relative to H3. e, ChIP-seq tracks of three PEGs - SU(VAR)3-9 HOMOLOG 7 (SUVH7), VARIANT IN METHYLATION 5 (VIM5) and YUCCA 10 (YUC10). f, Heatmap of PEG expression representing the asinh transform of the mean RNA-seq TPM values obtained from previously published datasets detailed in Supplementary Table 6. Sperm and egg were profiled with three and four biological replicates, respectively. g, Overlap enrichment of paternal or maternal biased genes in early zygotes with cluster 1, 2, 3 genes. Statistical enrichment was determined using pairwise two-sided Fisher’s exact tests. See source data for sample sizes (n) and precise p-values. h, 14h zygote transcript levels (log2 RNA-seq TPM) for genes expressed from cluster 1, 2, 3. Sample size (n = genes with TPM > 0.1) is denoted on each boxplot, which indicates minimum and maximum values as well as 25th, 50th and 75th quartiles. Statistical analysis was performed using two-sided Mann-Whitney U-tests. i, ChIP-seq tracks of three embryonic regulators - LEAFY COTYLEDON 1 (LEC1), FUSCA3 (FUS3) and WUSCHEL-RELATED HOMEBOX 2 (WOX2). In panels e and i, coverage represents log2 enrichment relative to input while coloured and grey shading indicate enriched or depleted signal, respectively. ChIP-seq data in b,c,d,e,i was performed using three biological replicates; two for sperm H3K27me3. j, Model for the H3K27me3 resetting mechanism in Arabidopsis sperm. This involves silencing of multiple PRC2 subunits, H3K27me3 demethylase activity and sperm-specific deposition of histone H3.10, which is immune to K27 methylation. The conjunction of these pathways leads to chromatin and transcriptional reprogramming of genes expressed during sperm differentiation and in the next generation. Statistical source data are provided in Source Data fig. 5.