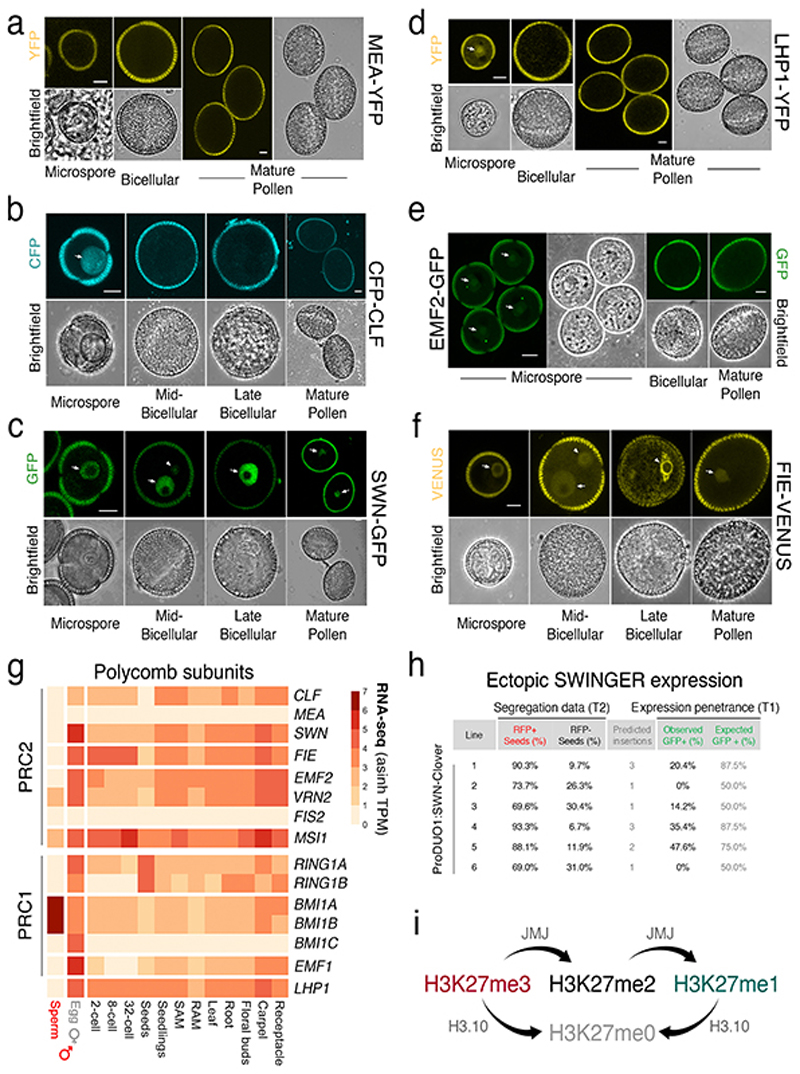
Extended Data Fig. 4.
Dynamics of the Polycomb machinery during sperm development.
a-f, Expression of MEA-YFP (a), CFP-CLF (b), SWN-GFP (c), LHP1-YFP (d), EMF2-GFP (e) and FIE-VENUS (f) during pollen development. All markers were absent from sperm at mature pollen stage. FIE had an appreciable signal in the sperm precursor but was excluded from the nucleus. Arrows indicate expression in the microspore or VN while arrowheads distinguish expression in the sperm lineage. Marker line analysis was repeated twice with independent inflorescences. Scale, 5 μm. g, Expression of Arabidopsis PRC2 (top panel) and PRC1 (bottom panel) subunits. Expression represents the inverse hyperbolic sine (asinh) transform of the mean RNA-seq TPM values obtained from previously published datasets detailed in Supplementary Table 6. Sperm and egg were profiled with three and four biological replicates, respectively. h, Ectopic expression of SWN-Clover under control of the sperm lineage-specific DUO1 promoter. Predicted insertions were estimated from T2 segregation of RFP fluorescent seeds arising from the pAlligatorR43 selection marker. Expression of SWN-GFP in T1 lines was barely detectable in pollen and well below that predicted from the T2 segregation data. i, Schematic of the action of JMJ proteins, which can demethylate H3K27 di-and tri-methylation but not mono-methylation. Statistical source data are provided in Source Data Extended data fig. 4.