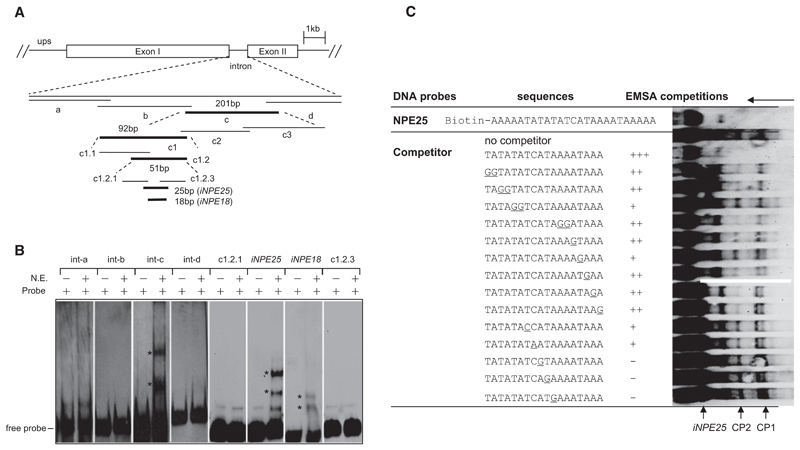
Figure 2. Identification of a Nuclear Protein-Binding Element in var Introns.
(A) EMSA screening strategy using biotin-labeled overlapping DNA fragments (bold sequences bound to nuclear proteins). The var intron (PF07_0048) containing a single repeat (RII-R1) was analyzed here. The sequences of the full-length intron and each probe are shown in Figure S1F and Table S4.
(B) A single intron region (iNPE25 or iNPE18) binds to nuclear proteins. The two iNPE-binding complexes (CP1 and CP2) were labeled with asterisks, respectively.
(C) Competition EMSA of biotin-labeled iNPE25 motif with various mutated nonlabeled iNPE18 sequences. Base pair exchanges in the mutated iNPE18 oligonucleotides are shown underlined. Competitor was used at a concentration of 100-fold excess of the labeled iNPE25 probe in each competition reaction. The decrease in intensity of CP1/CP2 bands was defined as strong (+++), medium (++), weak (+), and none (–), respectively, as shown in the table. Free probe, shifted bands CP1 and CP2, and running orientation of gel were labeled by arrows.