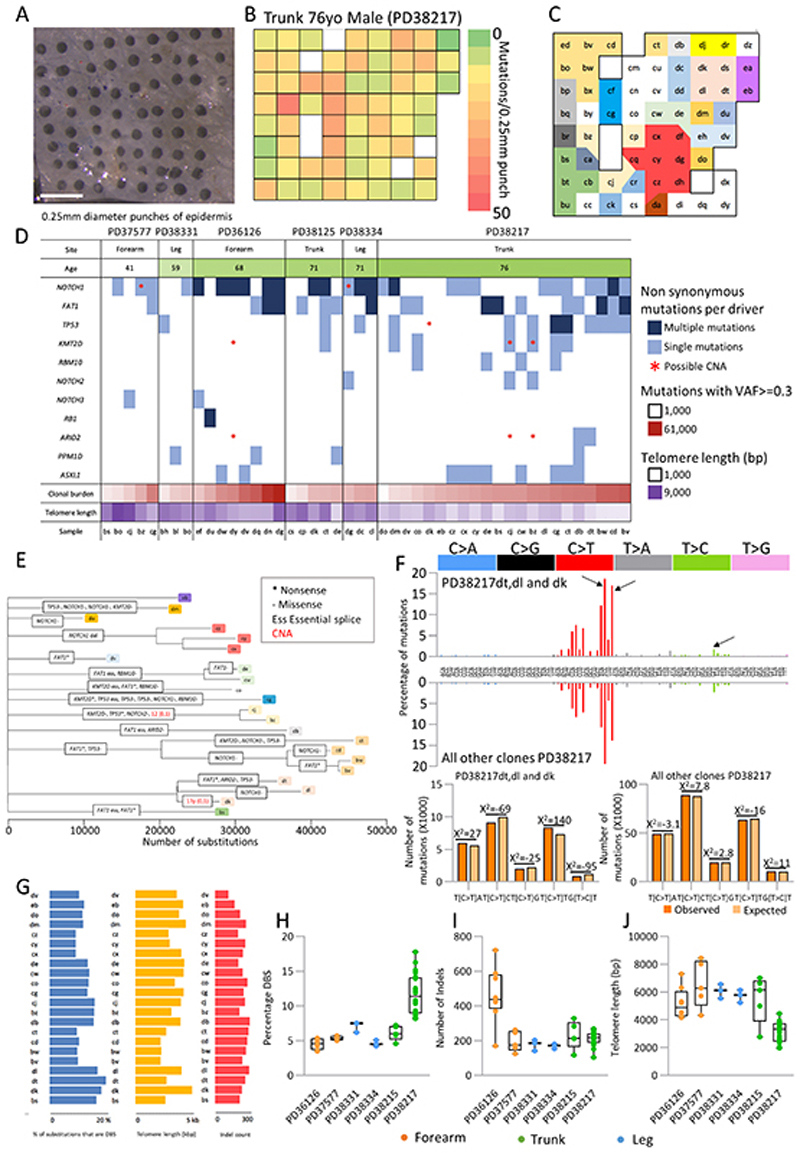
Figure 5. Variation in mutational load, mutational signatures and telomere length at fine scale resolution.
a. 0.25mm diameter punches were taken in a gridded array format from peeled epidermis. Samples were sequenced using a 324 gene bait panel and mutations identified using ShearwaterML as previously described. 232 punches from 6 individuals from leg, trunk and forearm were sequenced. A subset of samples were subsequently whole genome sequenced. Scale bar = 1mm.
b. Heat map of a single individual (Trunk 76yo male PD38217; shown in A) showing the number of mutations per 0.25mm punch detected from targeted sequencing.
c. Clonal map of the same individual as b. A filtered set of mutations with a variant allele fraction >= 0.2 was used to spatially map the clones, letters indicate individual samples, each color denotes a separate clone. White is used for polyclonal samples. Samples with too low DNA yield for sequencing have been removed from the map.
d. Plot summarising the mutations (VAF>=0.3) and copy number aberrations for genes identified as being under positive selection in targeted sequencing data for 46 wholegenome punch samples. Age of donor, number of clonal (VAF>=0.3) mutations and telomere length for each sample is shown. Not all events are independent as some samples are part of the same clone (Figure 5e, Figure S5).
e. Maximum parsimony tree of clonal substitutions detected in 32 whole-genome punch samples of trunk skin from a 76yo male (PD38217). Branch lengths are equivalent to the number of clonal single and double base substitutions and are annotated with clonal non-synonymous mutations detected in the 13 genes found to be under positive selection. Within each branch, driver mutations are arbitrarily ordered. Copy number alterations are shown in red.
f. Combined trinucleotide spectra for single base substitutions assigned to branches of the dt/dl/dk clade (top panel) versus those assigned to all other branches (bottom panel) from same individual as E (PD38217). Arrows show trinucleotide contexts found to differ the most between these two groups (chi-squared =397, d.f. =4, p=0). Clone dt, dl, dk = 49144 mutations, all other clones = 458479 mutations.
g. Variation in a single individual (PD38217) in the percentage of substitutions that are double base (DBS), telomere length and number of clonal (VAF of at least 0.3) insertion/deletions (indel) per whole genome sample.
h-j. Variation in the percentage of substitutions that are double base (h), number of insertions/ deletions (indel) (i) and telomere length (j) per whole genome sample, by donor. Three different body sites are shown: forearm (orange), trunk (green) and leg (blue).