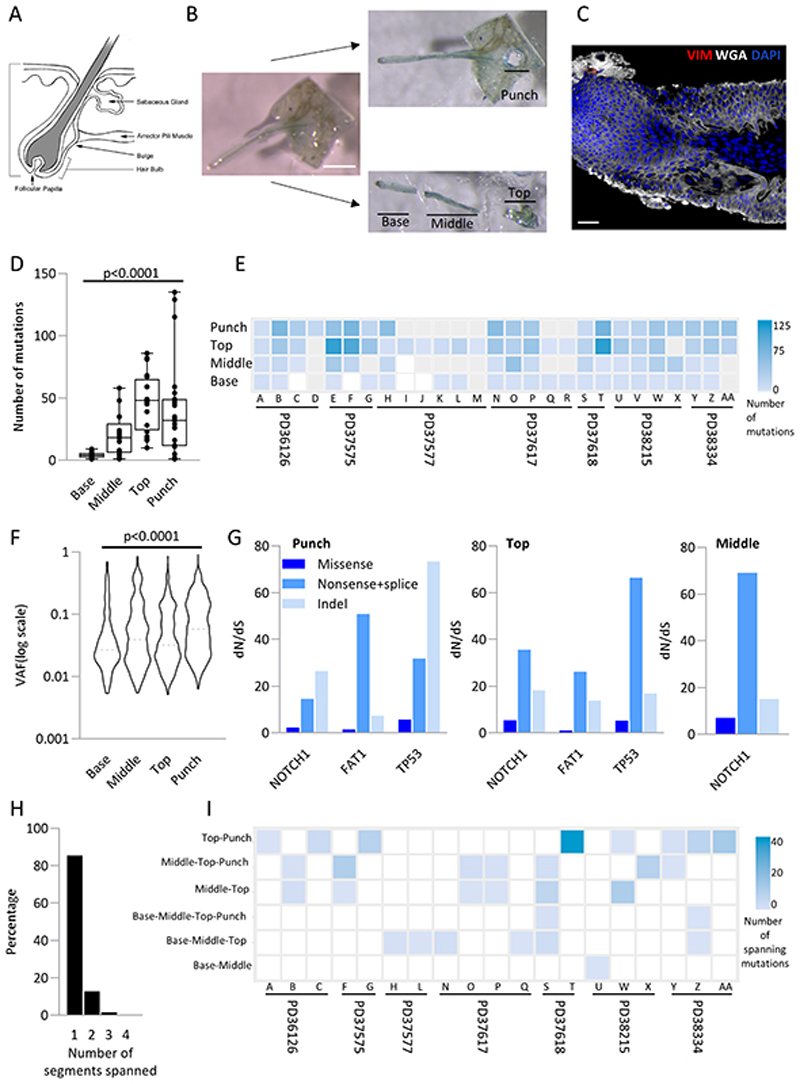
Figure 7. Human hair follicles are polyclonal with the base of the follicle showing differences in mutational load compared to the top.
a. Structure of the human hair follicle (https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/835470-overview)
b. Experimental outline: Intact hair follicles are dissected from the epidermis and cut into three (designated base, middle and top). A 0.25mm punch of epidermis was taken adjacent to the follicle (designated punch). All samples were sequenced at high depth using a 324 gene bait panel and mutations identified using ShearwaterML as previously. Scale bar = 0.5mm.
c. Example confocal image of hair follicle stained with WGA (white), Vimentin (red), and dapi (blue). Scale bar = 38μm
d. Distribution of the number of mutations in different parts of the follicle. Each dot represents a sample. Solid line indicates the median. p<0.0001 Kruskal-Wallis test.
e. Number of exonic mutations per follicle across 324 genes. Each column represents a follicle with patient noted below. Each row is either the punch, top, middle or base. Samples that had insufficient DNA for sequencing are shown as grey.
f. Violin plot of the variant allele frequency at each part of the follicle. Dashed line indicates the median. p<0.0001 Kruskal-Wallis test.
g. dN/dS ratios for missense, nonsense/ splice substitutions and insertions/deletions (indel) across different parts of the follicle. Only genes with globalq<0.01 are shown.
h. Percentage of mutations spanning more than one location (n=2009 mutations)
i. Heatmap of number of mutations spanning different segments of the hair follicle. Each column is a follicle with the patient indicated below. Only follicles with spanning mutations are shown (methods). Spanning segments are detailed on the left.