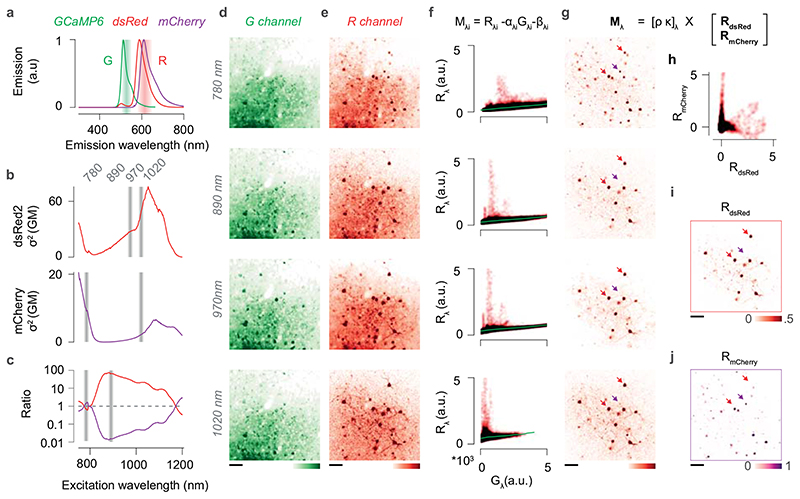
Extended Data Figure 6. Spectral unmixing of dsRed and mCherry fluorescence.
(a) Emission spectra of GCaMP6, dsRed and mCherry. Shaded areas indicate the emission band captured by the green (G) and red (R) channels of the microscope. Note that the G channel collects mostly GCaMP6 fluorescence, while the R channel captures a mixture of mCherry, dsRed and GCaMP6 fluorescence. Emission spectra were normalised to their peak. (b) Two-photon action cross-section of dsRed (top, red) and mCherry (bottom, purple). Shaded bands indicate the excitation wavelengths used for imaging: 780, 890, 970, and 1020 nm. (c) Ratio between the two-photon action cross-sections of dsRed and mCherry (red) and its inverse (purple). The four wavelengths used for imaging (dark red) were chosen to maximise the SNR of each fluorophore while ensuring the ratio between the two signals was maximal. (d) Example field of view imaged at the four excitation wavelengths in the G channel. GCaMP6 was expressed in all neurons with an AAV2.1-Syn-GCaMP6s in a GAD-NLS-mCherry mouse; a subset of presynaptic neurons was traced with a dsRed rabies virus. (e) Same as d, for the R channel. (f) The fluorescence in the R channel (R λ) plotted against the fluorescence in the G channel (G λ) for each pixel, and for each excitation wavelength λ. Because the GCaMP6 labelling was dense and both the dsRed and the mCherry signals were sparse, and because the contribution of dsRed and mCherry to Gλ was minimal, the GCaMP6 signal contributing to Rλ could be recovered by piecewise robust linear regression (αGλ + β). (g) The image representing the linear mix of dsRed or mCherry signals, F λ, was recovered by subtracting the scaled GCaMP6 image from the Rλ. (h) An iterative algorithm was used to linearly unmix the two source images. Each unmixing iteration was constrained to minimise the quadratic reconstruction error over the data and return maximally uncorrelated sources RdsRed and RmCherry. (I,j) The two source images RdsRed and RmCherry for the example field of view in d-e. Note that the unmixing procedure correctly recovers the nuclear localisation of mCherry without any prior. Scale bars are 50 μm. Similar results were obtained for all GAD-NLS-mCherry mice (N=4).