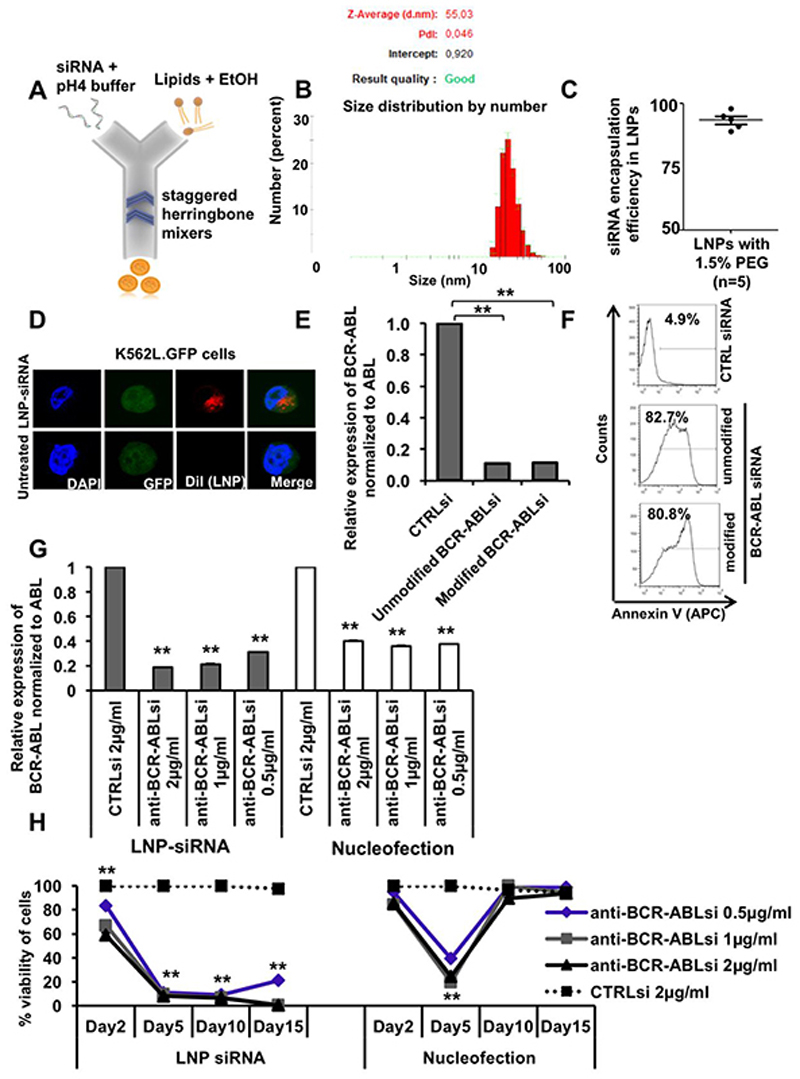
Figure 2. Formulation and characterization of lipid nanoparticle (LNP)-siRNA as an advanced delivery tool.
A. LNP-siRNA formulation scheme (outline). LNP components dissolved in ethanol were mixed with siRNA dissolved in low pH buffer in a microfluidic chip in the NanoAssemblr instrument.
B. Size distribution analysis of LNP-siRNA formulations produced with 1.5% PEG 2000 DMG (Peaks in the plot shows average diameter distribution, n=3).
C. Encapsulation efficiency of siRNA in LNPs, measured by the Ribogreen assay (n=5).
D. Subcellular distribution of LNP-siRNA (1 μg/ml) in K562L.GFP cells after 24 hours of incubation as shown by confocal imaging.
E. RT-PCR validation and comparison of BCR-ABL knockdown in K562L.GFP cells at 72 hours after nucleofection of 300nM unmodified and modified anti-BCR-ABL siRNA (mean ± SEM, n=3).
F. Representative FACS plot showing counts of Annexin V positive K562L.GFP cells at 96 hours after nucleofection of 300nM LNP-CTRL siRNA and anti-BCR-ABL siRNA (unmodified and modified/modification2).
G. Comparison of LNP versus nucleofection mediated siRNA delivery based on RT-PCR validation of BCR-ABL knockdown in K562L.GFP cells at 72 hours after siRNA delivery by LNPs (left side, grey bars) and by nucleofection (right side, white bars) (mean ± SEM, n=3).
H. Comparison of LNP versus nucleofection mediated siRNA delivery based on viability of K562L.GFP cells at day 2, 5, 10 and 15 after siRNA delivery (mean ± SEM, n=3).
** indicates P<.01