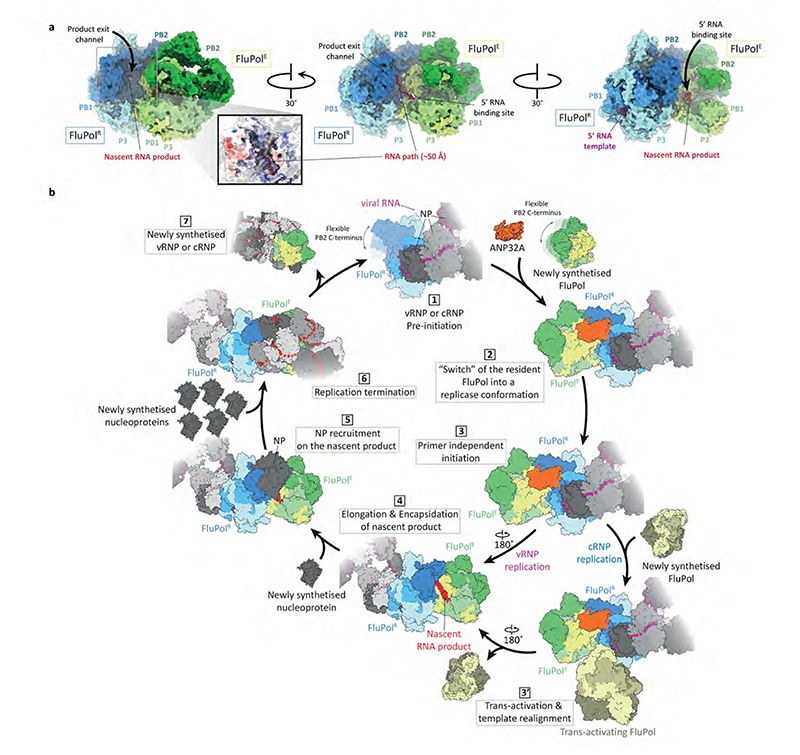
Fig. 4. Functional implications of the FluPolC-ANP32A complex.
a, Relative positions of the RNA product exit channel in FluPolR and the 5’ RNA binding site in FluPolE in the chANP32A-FluPolC complex. The positions of the RNA product exit channel in FluPolR and the 5’ RNA binding site in FluPolE were determined by superposing FluPolR and FluPolE with the structure of FluPolA bound to capped RNA and vRNA template (PDB 6RR7). b, Model for the role of FluPol-ANP32A complex in the replication of the influenza virus RNA genome and its assembly into RNP. FluPol in the context of vRNP or cRNP is flexible (1) but is stabilised in a replicase FluPolR conformation upon binding of a newly synthesised FluPol in the presence of ANP32A (2). FluPolR initiates replication in a primer independent manner (3) with a trans-activating FluPol involved in cRNA to vRNA replication by promoting cRNA template realignment (3’). As the 5’ end of the nascent replication product is released from the polymerisation active site of FluPolR, it is captured in the 5’ RNA binding pocket of the encapsidating FluPolE bound to FluPolR (4), initiating the encapsidation of the nascent RNA with NP (5). Nascent vRNA or cRNA assemble into vRNP or cRNP, respectively (6), and are released upon FluPolR termination. FluPolE becomes the resident polymerase of the newly produced vRNP or cRNP.