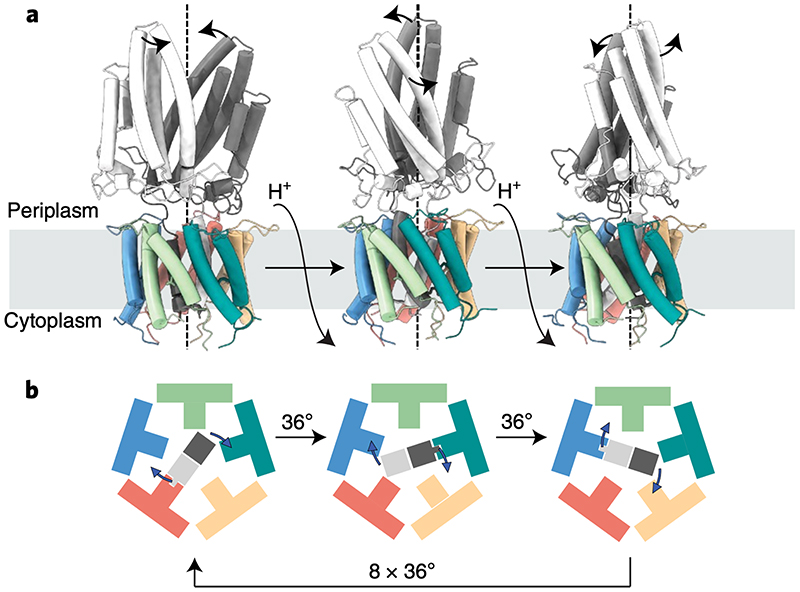
Fig. 6. Model for the mechanism of coupling proton flow to GldM rotation in the GldLM motor.
a, GldLM′ is shown in a cartoon representation, coloured as in earlier Figures. Panels represent the model after successive 36° rotations of the GldM′ subunits driven by net flow of a single proton down the transmembrane proton electrochemical gradient.
b, The transmembrane domain of the motor is shown schematically viewed from the cytoplasm and coloured as in a. The central GldM dimer rotates within the GldL pentamer in 36° steps driven by proton flow. 10 steps in total are required to bring the GldM dimer back to the starting position. At each step a salt bridge is present between one GldM chain and one GldL chain. This binding interaction is represented by the fit of the GldM chain into a GldM-binding box on the GldL subunit. The direction of rotation shown is arbitrary.