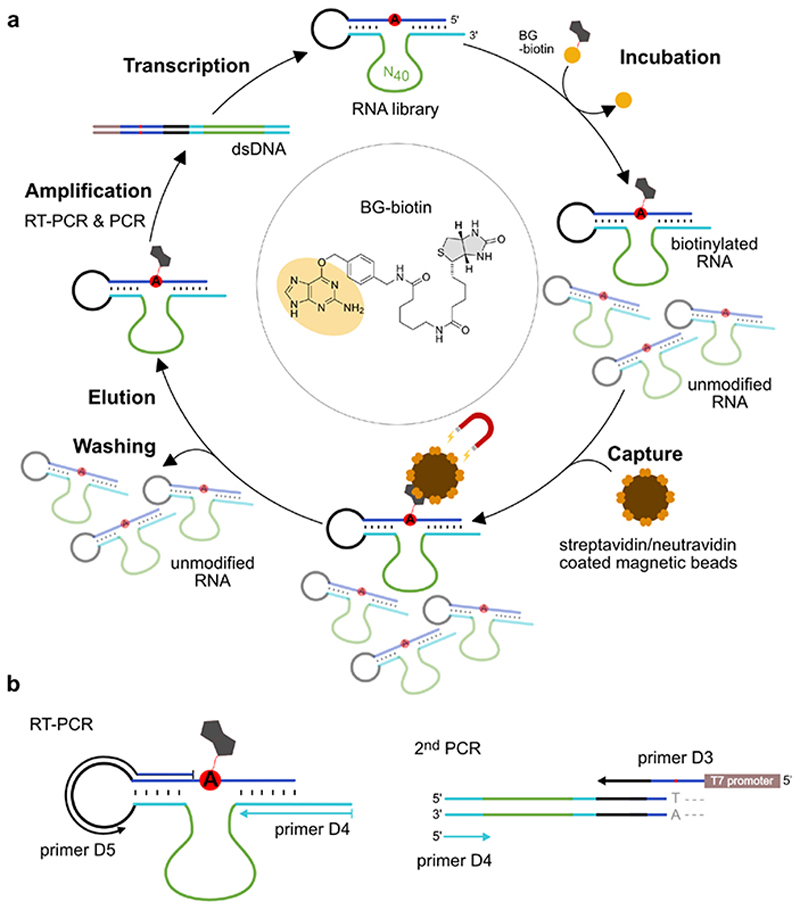
Figure 1. Extended Data Figure 1.
a. In vitro selection scheme consisting of incubation, capture, wash, elution, amplification and transcription steps. The RNA substrate (blue) contains an unpaired adenosine (red, A) and is connected to the RNA library via the single-stranded loop (black). The library contains 40 random nucleotides (green) and two constant binding arms (cyan) complementary to the RNA substrate upstream and downstream of the bulged A. Incubation: 50 μM RNA, 100 μM SNAP-biotin, 50 mM HEPES, pH 7.5, 120 mM KCl, 5 mM NaCl, 40 mM MgCl2, 37°C. (Round 1-8: 16 h; Round 9-11: 4 h; Round 11: 50 μM SNAPbiotin). Capture: Beads were blocked with E. coli tRNA; streptavidin and neutravidin beads were switched every other round. Denaturing wash buffer: 8 M urea, 10 mM Tris.HCl, pH 7.5, 1 mM EDTA, 0.01% tween-20; Elution: 95% formamide, 1 mM EDTA, 95°C, 5 min. b. RT-PCR: 42°C, 30 min, 10 cycles PCR with 1 μM primer D4 and 0.5 μM primer D5. 2nd PCR: 25 cycles, 5% (v/v) RT-PCR product as template, 1 μM D4 and 0.5 μM D3, 10% (v/v) DMSO, annealing temp. 65°C. In vitro transcription: dsDNA template from 200 μL PCR reaction, 100 μL reaction volume with 4 mM each NTP, followed by PAGE purification.