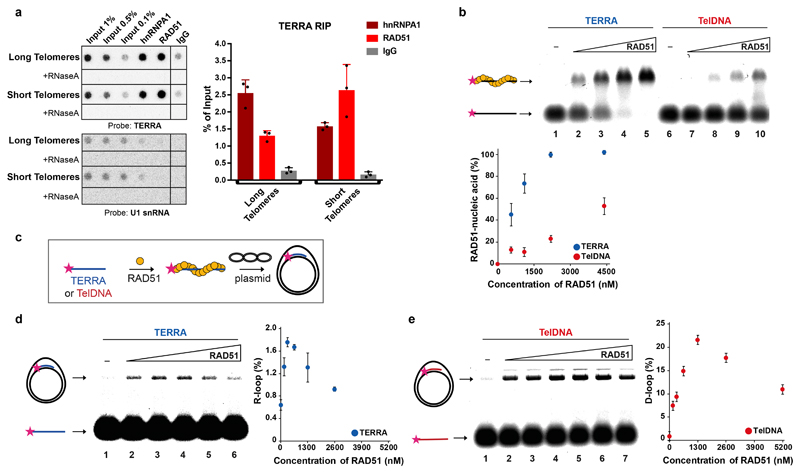
Fig. 3. RAD51 associates with TERRA and catalyzes R-loop formation.
a, Native RNA-immunoprecipitation (RNA-IP) assay with anti-RAD51 and anti-hnRNPA1 antibodies performed in extracts from HeLa cell clones with long or short telomeres. Western blotting was used to evaluate the IP efficiency of RAD51 and hnRNPA1, and co-IP of BRCA2 (see Extended data Fig. 7c, d). IP-recovered RNA was analyzed for TERRA and U1 snRNA. n=3 biologically independent experiments, data are mean ± s.d. Two-tailed unpaired t test was used to calculate the P values. (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001). b, Affinity of RAD51 for TERRA (lanes 1 – 5) and TelDNA (lanes 6 – 10) oligonucleotides analyzed by EMSA. Fluorescently labelled RNA or DNA substrates (20 nM) were incubated with increasing concentration of RAD51 protein (550, 1100, 2200, and 4400 nM). Quantification is shown on the bottom. n=3 independent experiments, data are mean ± s.d. c, Schematics for R-loop and D-loop formation assay. d, RAD51 concentration dependent formation of R-loops, its detection on native gel and quantification. n=3 independent experiments, data are mean ± s.d. e, Detection of D-loops on native gel and quantification. n=3 independent experiments, data are mean ± s.d.