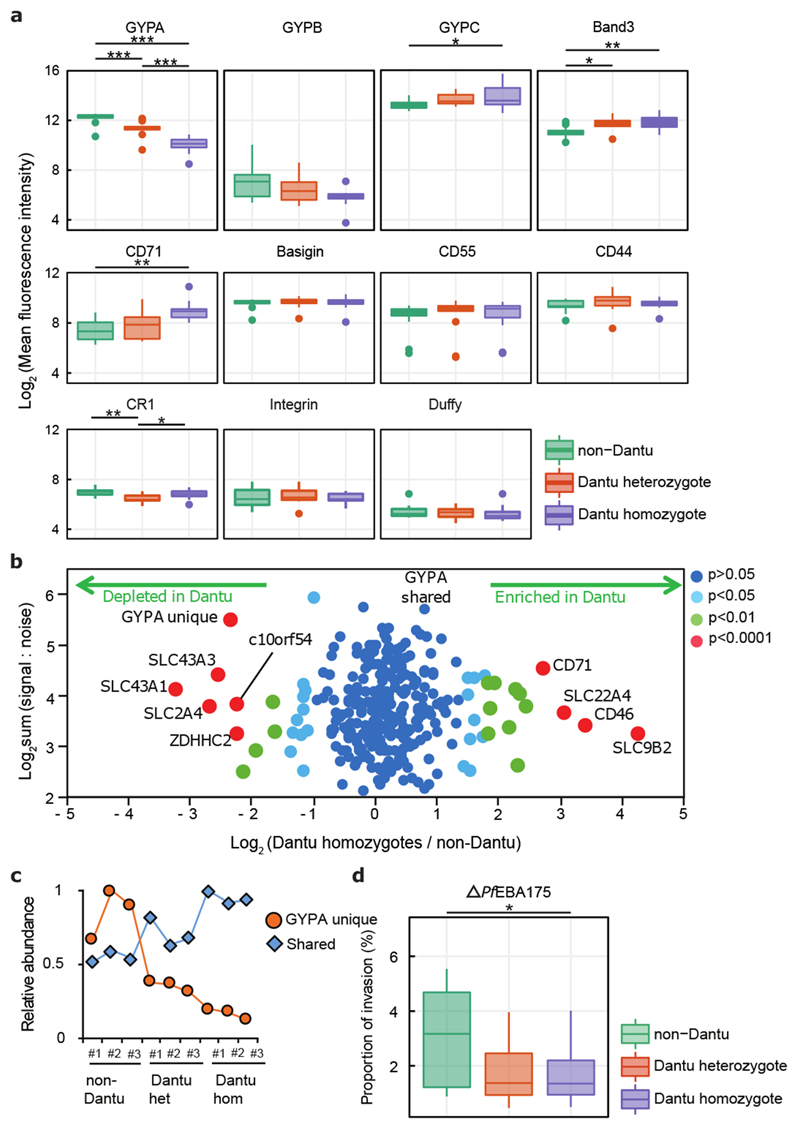
Figure 2. RBC membrane protein characteristics vary across Dantu genotypes but do not directly correlate with invasion efficiency.
(a) The relative expression of essential RBC membrane proteins was assessed using fluorescent monoclonal antibodies in flow cytometry assays. 13 non-Dantu, 12 Dantu heterozygotes and 11 Dantu homozygotes were tested. Statistical comparison across groups was performed by one-way ANOVA, while pairwise comparisons between groups used the Tukey HSD test. Significant differences were observed in GYPA (non-Dantu vs. Dantu homozygote p=6.25×10−11; non-Dantu vs. Dantu heterozygote p= 4.62×10−6; Dantu heterozygote vs. Dantu homozygote p= 6.86×10−4), GYPC (non-Dantu vs. Dantu homozygote p=0.03), Band3 (non-Dantu vs. Dantu homozygote p=6.25×10−11; non-Dantu vs. Dantu heterozygote p=0.0136), CD71 (non-Dantu vs. Dantu homozygote p=0.006), and CR1 (non-Dantu vs. Dantu heterozygote p=0.003; Dantu heterozygote vs Dantu homozygote p=0.045). (b) Scatter plot of all proteins quantified by mass spectrometry (n=3 RBCs per genotype). Fold change was calculated by average signal:noise (Dantu homozygote/non-Dantu). GYPA was split into two parts: identified by peptides unique to GYPA (‘GYPA unique’, originating from extracellular region) or shared with the Dantu protein (‘GYPA shared’, originating from intracellular region). Mass spectra were processed with the quantitative proteomics platform “MassPike” and the method of significance A with Benjamini-Hochberg multiple testing correction was used to estimate the p-value that each protein ratio was significantly different to 1. (c) Graph of the relative abundance of ‘unique’ and ‘shared’ GYPA peptides across all donors. Signal:noise values were normalised to a maximum of 1 for each protein. Statistical data for (b) and (c) listed in Supplementary Table 4. (d) Comparison of invasion efficiency of a genetically modified parasite strain, ΔPfEBA175, across genotypes (n=13 non-Dantu, 12 Dantu heterozygotes and 12 Dantu homozygotes) using the flow-cytometry-based preference invasion assay. The percentage of parasitised RBCs in each genotype is indicated on the y-axis. Statistical comparison across groups was by one-way ANOVA, while pairwise comparisons between groups used the Tukey HSD test (non-Dantu vs. Dantu homozygote p=0.04). ** p < 0.01; * p < 0.05.