Figure 1. PPGNTS neurons selectively encode large meal satiation.
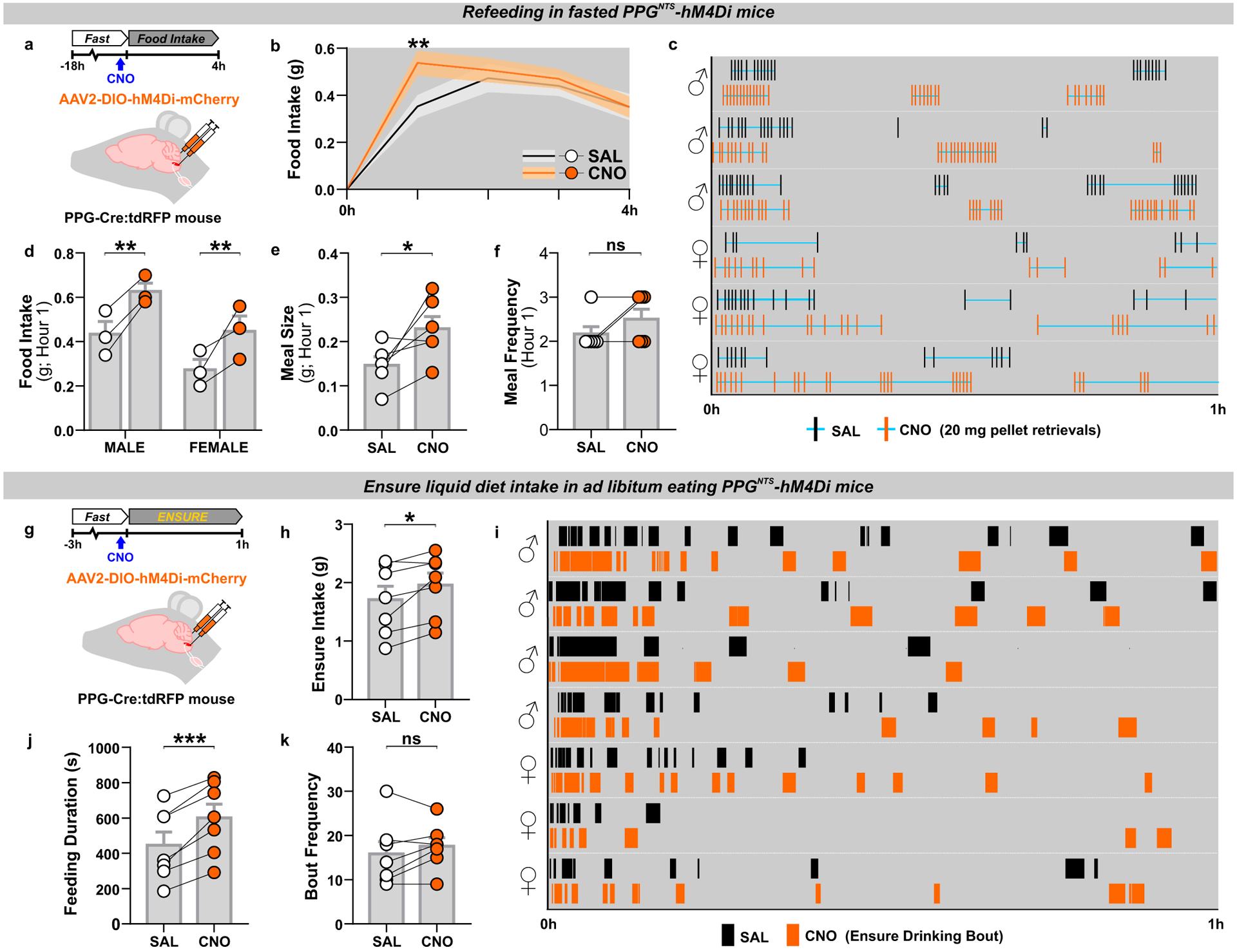
(a) Experimental model and paradigm for meal pattern analysis of post-fast refeeding in PPGNTS-hM4Di mice using FED system. n=6 animals for analyses presented in b-f.
(b) 4h dark phase food intake, 2-way within-subjects ANOVA: Drug × Time F(3,15)=3.664, p=0.0367.
(c) Raster plot of chow pellet retrievals over 1h dark phase. Plots from the same mouse after saline and CNO injections presented adjacently.
(d) 1h intake by sex, 2-way mixed-model ANOVA: Drug F(1,4)=29.09, p=0.0057.
(e-f) Meal pattern parameters during 1h refeed, paired 2-tailed t-test or Wilcoxon matched-pairs test: E) t(5)=2.757, p=0.040; F) W=−3, p=0.500.
(g) Experimental model and paradigm for temporal analysis of Ensure intake in PPGNTS-hM4Di mice. n=7 animals for analyses presented in h-k.
(h) 1h Ensure intake, paired 2-tailed t-test: t(6)=2.859, p=0.0288. Ensure intake was sex-independent, 2-way mixed-model ANOVA: Sex × Drug F(1,5)=2.553, p=0.171.
(i) Raster plot of Ensure drinking bouts over 1h dark phase. Plots from the same mouse after saline and CNO injections presented adjacently.
(j-k) Temporal parameters of Ensure drinking, paired 2-tailed t-test: J) t(6)=6.55, p=0.0006; K) t(6)=1.263, p=0.254; M) t(6)=4.784, p=0.0031.
All data presented as mean ± SEM.
