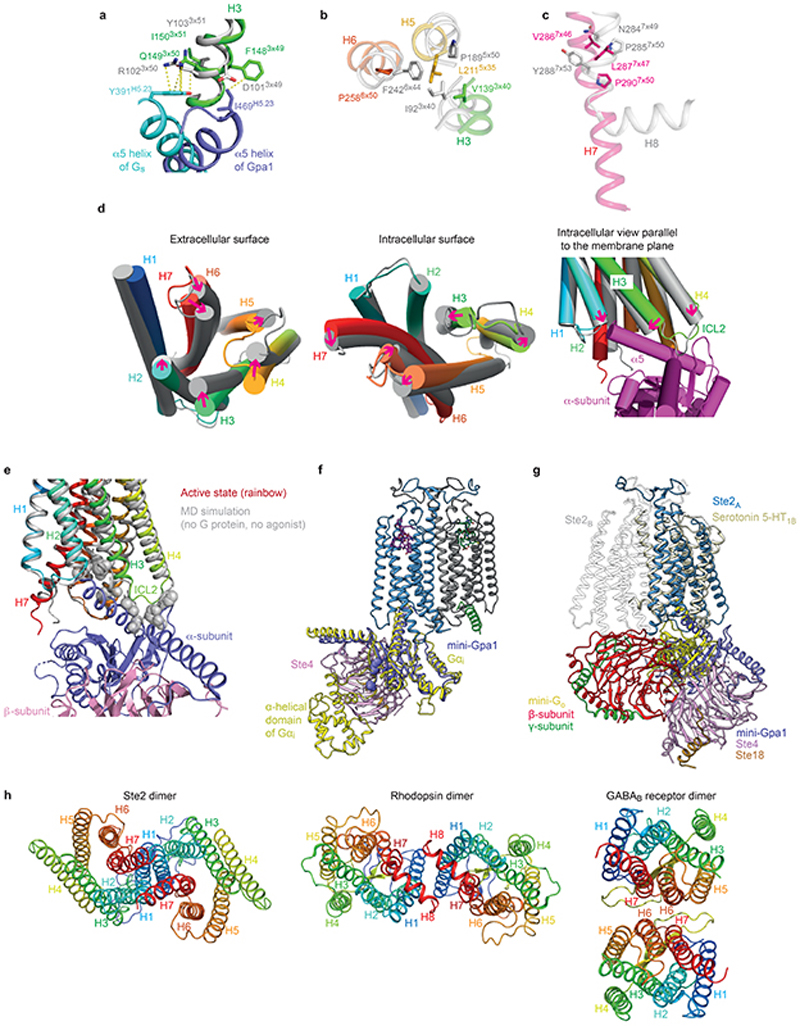
Extended Data Fig. 9. Structural features of Ste2 and comparison with mammalian GPCRs.
a-c, Alignment of GPCRs was performed by GESAMT74 (CCP4 suite of programs) in conjunction with 39 other G protein or arrestin-coupled GPCR structures (Fig. 5a). Ste2 is depicted in rainbow colouration and the adenosine A2A receptor (A2AR) in grey. a, DRY motif showing the stacking (van der Waals contacts, yellow dashed lines) of the highly conserved Arg3×50 residue with PheH5.23 of the α-subunit of Gs. b, Pro5×50-Ile3×40-Phe6×44 motif provides a conserved packing of residues in the active state at the core of Class A receptors. A similar role could be played by Leu5×35 and Val3×40 in Ste2. c, the NPxxY motif in Class A GPCRs aligns with a conserved region in Ste2 receptors (see also Extended Data Fig. 6a), but Pro7×50 in Ste2 is not associated with a kink in H7 as it does in Class A GPCRs. d, Conformational changes in the transmembrane α-helices observed during MD simulations of the dimer without the G proteins or the ligands. e, Alignment of the active state Ste2 (rainbow coloration) with the Ste2 conformation (grey) reached after MD simulations in the absence of G protein and ligand. Gpa1 would not be able to couple to this new conformation due to clashes with atoms in H2 (Ile80), H3 (Phe148, Gln149, Lys151, Val152, Thr155) and ICL2 (Gly156, Asp157, Asn158, Phe159). Clashes are defined as atoms (grey spheres) within 2 Å of atoms in Gpa1 coupled to the active state of Ste2. f, The position of the α-helical domain in Gpa1 distal to the dimer interface can be inferred from comparison with the structure of Gi (yellow) coupled to rhodopsin (PDB code 6CMO) after alignment with mini-Gpa1 (purple). The position in Gpa1 of the deletion of the α-helical domain (which also includes the ubiquitination domain) is indicated by the amino acid residues immediately before and after the deletion being shown as spheres. g, superposition of Go-coupled serotonin 5-HT1B receptor (yellow) with Ste2A (blue). The position of heterotrimeric Go does not align with the yeast G protein and is sited below Ste2B (grey). h, Views of the intracellular surfaces of dimers from Class D (Ste2), Class A (rhodopsin; PDB code 6OFJ) and Class C (GABAB receptor; PDB code 7C7Q). All receptors are in rainbow coloration.