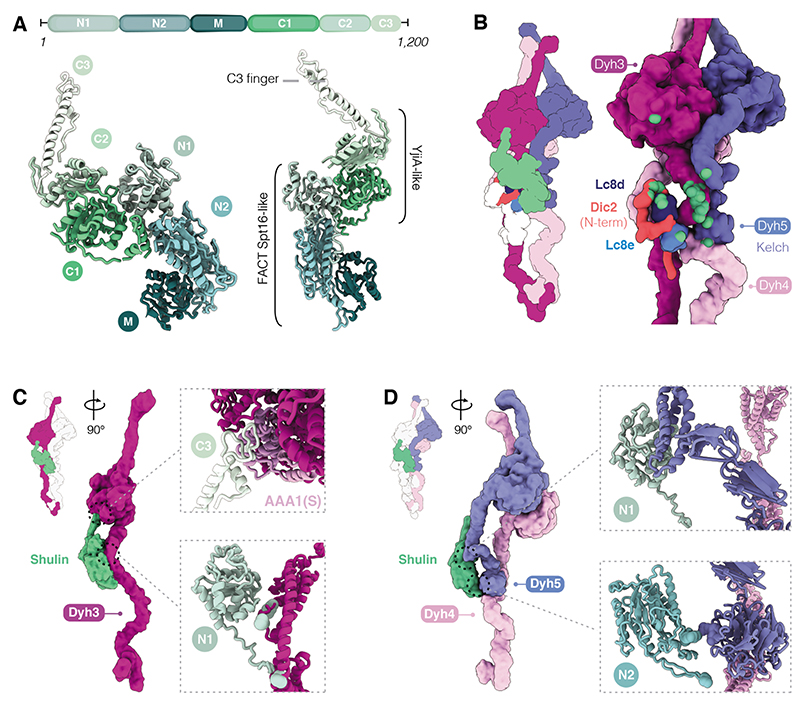
Fig. 4. Characterization of Shulin structure and its mechanism of ODA inhibition.
(A) Domain architecture of Shulin. N-terminal (N1, N2) and Middle (M) domains share a similar fold with the FACT complex core subunit Spt16. C-terminal (C1, C2) domains are similar to GTPase YjiA and are followed by a C-terminal finger (C3). (B) Cartoon and filtered surface representation with main contacts between Shulin and ODA subunits highlighted in green spheres. (C) Shulin’s N1 domain contacts helical bundles proximal to the linker in Dyh3 tail. The C3 finger projects out to contact Dyh3 AAA1(S) (insets). (D) Shulin’s N1 domain contacts Dyh5 helical bundles and its N2 domain touches the Kelch domain. Shulin contacts Dyh4 just below Dyh5 Kelch-domain (insets).