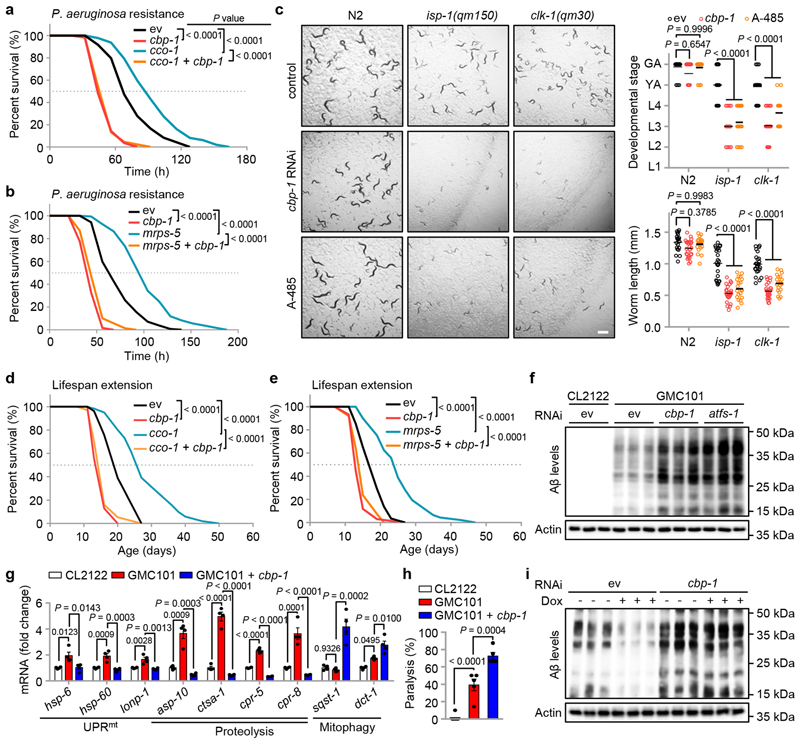
Fig. 4. CBP-1 is essential for mitochondrial surveillance, MSR-associated immune response, lifespan extension and amyloid-β proteotoxicity reduction.
a, b, The impact of cbp-1 knockdown on mitochondrial stress-induced P. aeruginosa resistance. Survival of worms fed with control (ev) or cbp-1 (20%) RNAi, in combination with cco-1 (50%) (a) or mrps-5 (80%) (b) RNAi, and exposed to P. aeruginosa. c, Representative photos of wild-type (N2), isp-1(qm150) or clk-1(qm30) worms fed with control, cbp-1 (10%) RNAi or treated with A-485 (10 μM) since maternal L4 stage. The developmental stage and body length of the F1 progeny were quantified at Day 4 after hatching (n = 25 worms for each condition). Scale bar, 1 mm. GA, gravid adult; YA, young adult; L1-4, larval stage 1-4. d, e, The impact of cbp-1 knockdown on mitochondrial stress-induced lifespan extension. cbp-1 RNAi attenuates lifespan extension induced by cco-1 (50%) (D) or mrps-5 (50%) (E) RNAi. RNAi targeting cbp-1 occupies 20% (d) or 10% (e). f, g, estern blots of Aβ aggregation and Actin levels (f), and transcript levels of selected genes measured by qRT-PCR (n = 4 biologically independent samples) (g) of CL2122 or GMC101 worms fed with control, cbp-1 (10%) or atfs-1 RNAi. h, Percentage of paralysis of CL2122 or GMC101 worms fed with control or cbp-1 (10%) RNAi at Day 5 of adulthood (n = 5 independent experiments). i, The impact of cbp-1 knockdown on mitochondrial stress-induced Amyloid-β proteotoxicity reduction. estern blots of Aβ aggregation and Actin in GMC101 worms fed with control or cbp-1 (10%) RNAi with or without Dox (15 μg/ml) treatment. Error bars denote SEM. Statistical analysis was performed by ANOVA followed by Tukey post-hoc test in (c, g, h), or log-rank test in (a, b, d, e). For uncropped gel source data, see Source Data Fig. 4.