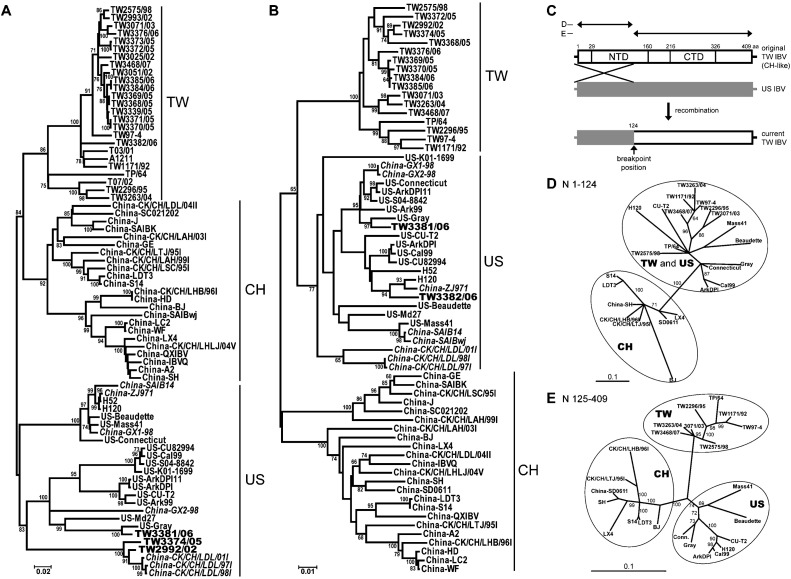
Fig. 1.
Phylogenetic relationships among the IBVs. (A and B) Phylogenetic trees based on ME algorithms on the full-length S1 (A) and full-length N genes (B) show the relationships among the three major IBV groups, Taiwanese (TW), Chinese (CH) and American (US). Bootstrap values, estimated from 1000 replicates of the ME analysis in MEGA 4.0, are given in percentage (%). The default setting of the MEGA program chooses the longest branch as the root. Scale bar indicates the number of nucleotide replacements per site. Exceptional TW strains are marked in bold. (C) Diagram illustrating RNA recombination in TW IBVs. NTD, N-terminal domain; CTD, C-terminal domain. (D and E) The phylogenetic analyses of the crossover (aa 1–124) (D) and non-crossover regions (aa 125–409) (E) of the N protein were based on BI analysis in MrBayes 3.1.2. The scale bars correspond to the number of amino acid replacements per site.