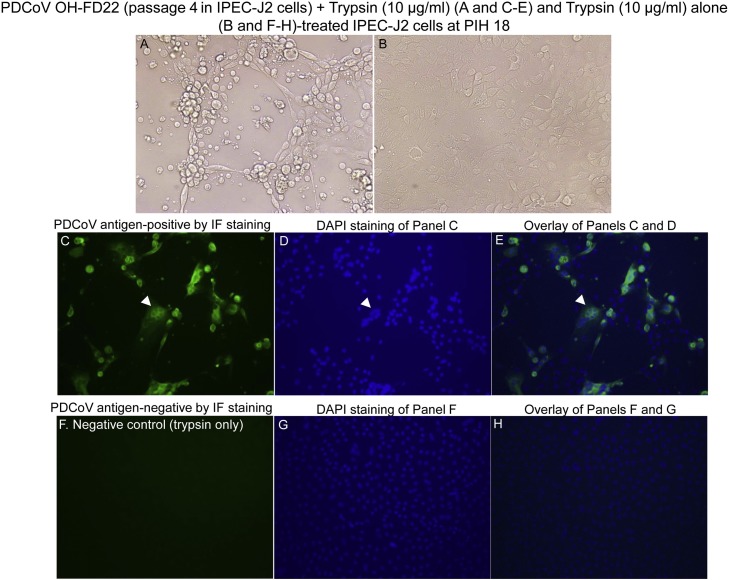
Fig. 1.
Cytopathic effects (CPE) and localization of PDCoV antigens by immunofluorescent (IF) staining in the IPEC-J2 cells inoculated with the PDCoV strain OH-FD22 during the 4th serial passage, and supplemented with 10 μg/ml of trypsin in the cell culture medium. (A) PDCoV OH-FD22-inoculated IPEC-J2 cells at post-inoculation hour (PIH) 18, showing CPE that consists of enlarged, rounded, and densely granular cells that occurred singly or in clusters, often forming cell clumps, followed by cell shrinkage and detachment. (B) PDCoV-uninoculated IPEC-J2 cells supplemented with 10 μg/ml of trypsin showing normal cells. (C) IF staining of the inoculated IPEC-J2 cells at PIH 18, showing that the enlarged, rounded, and clustered cells are positive for PDCoV antigen (green staining). (D) Blue-fluorescent 4′, 6-diamidino-2-phenylindole dihydrochloride (DAPI) staining of Panel C to counterstain nuclear DNA. (E) Overlay of Panels C and D. Note that the entire clustered cells positive for PDCoV antigen (arrowheads) appeared to be syncytial or multinucleated cells. (F) IF staining of PDCoV-uninoculated, trypsin (10 μg/ml)-treated IPEC-J2 cells at PIH 18, showing no cells positive for PDCoV antigen. (G) DAPI staining of Panel F. (H) Overlay of Panels F and G. Original magnification, all ×200.