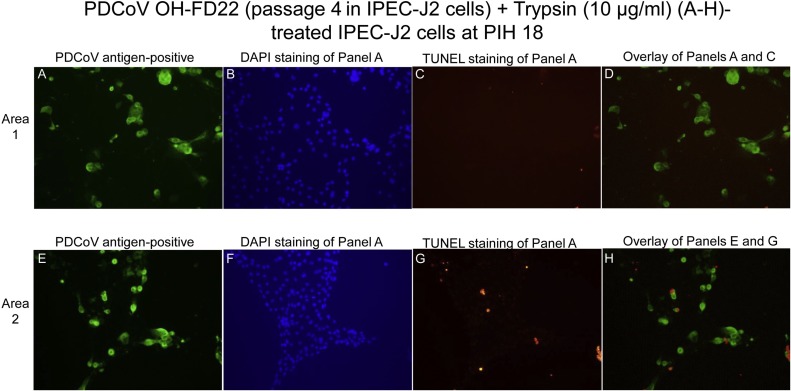
Fig. 2.
Localization of PDCoV antigens by immunofluorescent (IF) staining and apoptotic cells by a TUNEL assay in the IPEC-J2 cells inoculated with the PDCoV strain OH-FD22 during the 4th serial passage, and supplemented with 10 μg/ml of trypsin in the cell culture medium. (A) IF staining of the inoculated IPEC-J2 cells at post-inoculation hour (PIH) 18, showing that the enlarged, rounded, and clustered cells are positive for PDCoV antigen (green staining). (B) Blue-fluorescent 4′, 6-diamidino-2-phenylindole dihydrochloride (DAPI) staining of Panel A. (C) Double TUNEL staining of Panel A, showing that most of the cytopathic effect (CPE)- and PDCoV antigen-positive cells are TUNEL (intranuclear red staining)-negative. (D) Overlay of Panels A and C, showing that few PDCoV antigen-positive cells are TUNEL-positive (intranuclear red staining); however, most of the PDCoV antigen-positive IPEC-J2 cells did not show TUNEL-positive signals, indicative of no positive correlation of PDCoV antigens with TUNEL signals. (E) IF staining of the inoculated IPEC-J2 cells at PIH 18 (other microscopic area that differs from Panels A–D), showing that the enlarged, rounded, and clustered cells are positive for PDCoV antigen (green staining). (F) DAPI staining of Panel A. (G) Double TUNEL staining of Panel A, showing that a number of the CPE- and PDCoV antigen-positive cells are TUNEL (intranuclear red staining)-negative. (H) Overlay of Panels A and C, showing that a few PDCoV antigen-positive cells are TUNEL-positive (intranuclear red staining); however, most of the PDCoV antigen-positive IPEC-J2 cells did not show TUNEL-positive signals, indicative of little or no positive correlation of PDCoV antigens with TUNEL signals. Original magnification, all ×200. TUNEL, terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick end labelling.