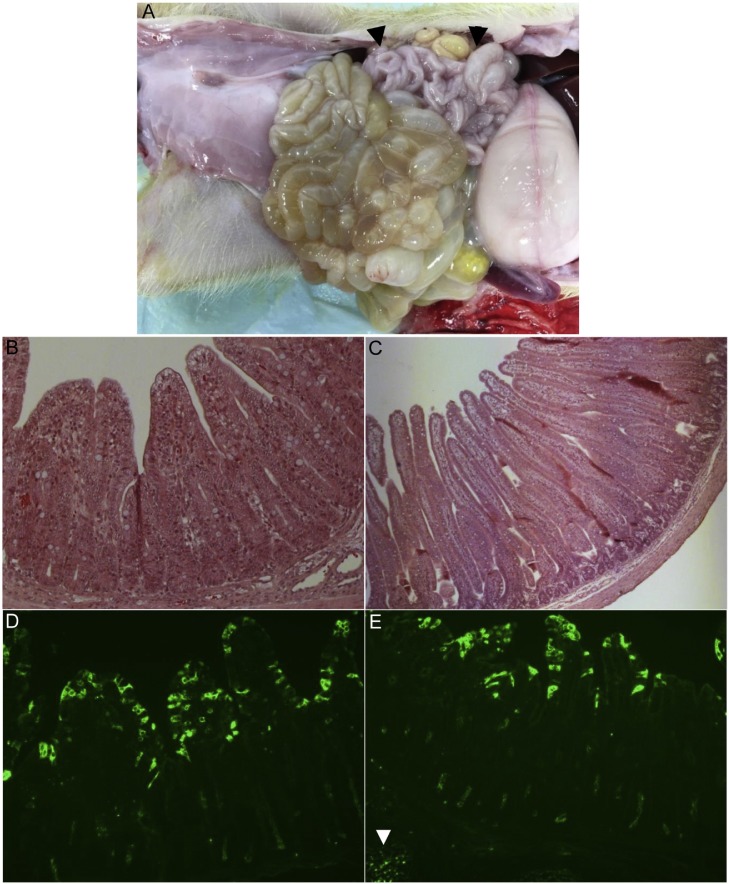
Fig. 4.
Gross and histological lesions and detection of PDCoV antigen by immunofluorescent (IF) staining in the intestine of 10-day-old gnotobiotic pigs inoculated orally with the IPEC-J2 cell culture-passaged PDCoV (OH-FD22-P8-I-P4) or mock. (A) Intestine of PDCoV-inoculated pig 1 at post-inoculation day (PID) 5, showing thin and transparent intestinal walls and luminal accumulation of large amounts of watery liquid in the small [but with lack of lesions in the duodenum to proximal jejunum close to the pylorus (arrowheads)] and large intestine. (B) Hematoxylin and eosin-stained mid-jejunum of PDCoV-inoculated pig 1 at (PID) 5, showing severe atrophic enteritis. (C) Hematoxylin and eosin-stained mid-jejunum of mock-inoculated pig 3 at PID 5, showing normal villous epithelium. (D) IF-stained mid-jejunum of PDCoV-inoculated pig 1 at PID 5, showing moderate numbers of PDCoV antigen-positive cells (green color) in the villous epithelium. (E) IF-stained ileum of PDCoV-inoculated pig 1 at PID 5, showing low numbers of PDCoV antigen-positive cells (green color) in the villous epithelium. Note low numbers of PDCoV antigen-positive cells in the Peyer’s patch (arrowhead). Original magnification, ×200 (panels B, D, and E) or ×80 (panel C).