Fig. 1.
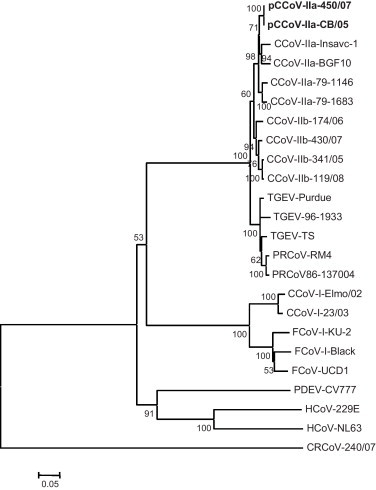
Neighbour-joining tree based on the spike protein of members of genus Alphacoronavirus. For phylogenetic tree construction, the following CoV strains were used (GenBank accession numbers are reported in parentheses): porcine transmissible gastroenteritis virus (TGEV) Purdue (NC_002306), TS (DQ201447), 96-1933 (AF104420); porcine respiratory coronavirus (PRCoV) RM4 (Z24675), 86-137004 (X60089); CCoV-IIa CB/05 (DQ112226), Insavc-1 (D13096), BGF10 (AY342160); CCoV-IIb 341/05 (EU856361), 174/06 (EU856362), 430/07 (EU924790), 118/08 (EU924791); CCoV-I Elmo/02 (AY307020), 23/03 (AY307021); feline coronavirus (FCoV) type I Black (EU186072), KU-1 (D32044), UCD-1 (AB088222); FCoV-II 79-1146 (NC_007025), 79-1183 (X80799); HCoV-229E (NC_002645), PEDV-CV777 (NC_003436), HCoV-NL63 (NC_005831). The tree is rooted on the Betacoronavirus canine respiratory coronavirus (CRCoV) 240/05 (EU999954). A statistical support was provided by bootstrapping over 1000 replicates. The scale bars indicate the estimated numbers of amino acid substitutions per site.
