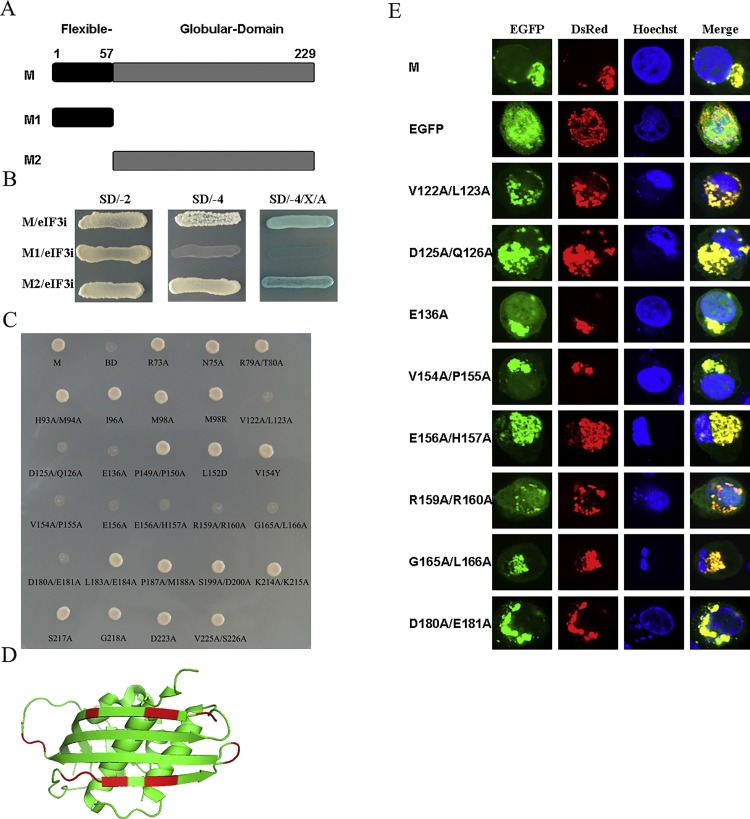
Fig. 2.
The region of M that interacts with eIF3i is located within the 122- to -181 amino acids.
(A) Schematic diagram showing the M domains tested in this study. (B) Y2H screens were performed to confirm the interaction between the eIF3i protein and the flexible domain (amino acids 1–57) and the globular domain (amino acids 58 to 229) of M protein. (C) Analysis of the interaction between the mutants of M with eIF3i in a yeast two-hybrid system. AH109 yeast cells co-transfected with the indicated bait and prey plasmids were streaked onto QDO (SD/–Ade/–His/–Leu/–Trp) plates, and the clones were determined after 72 h. (D) The residues involved in the M-eIF3i interaction were shown in red. (E) Analysis of the interaction between mutants of M with eIF3i by confocal microscopy assay. The cells were co-transfected with the indicated bait and pT-DsRed-eif3i plasmids and then fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde at 24 h post-transfection. The results were obtained with a laser confocal scanning microscope. Each experiment was repeated at least three times. BD, pGBKT7 empty vector; SD/-2, SD/-Leu/-Trp; SD/-4, SD/-Ade/-His/-Leu/-Trp; SD/-4/X/A, SD/-Ade/-His/-Leu/-Trp/X-a-Gal/Aureobasidin A.(For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)