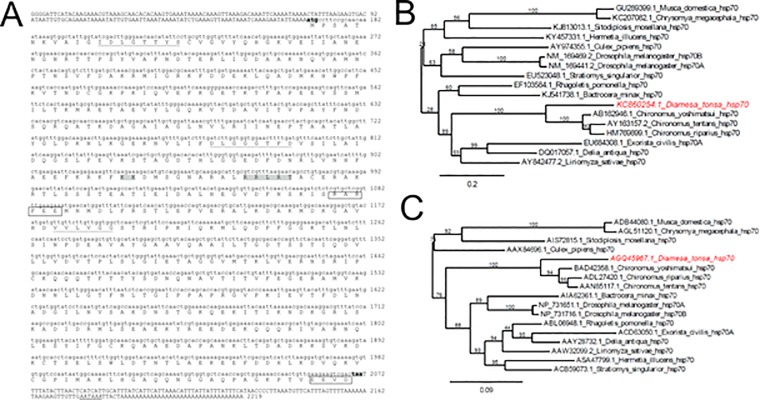
Fig 1. Characterization of hsp70 gene in Diamesa tonsa.
(A) Nucleotide sequence of the hsp70 gene in D. tonsa with deduced amino acid sequence. In the nucleotide sequence, upper case indicates the 5ʹUTR and the 3ʹUTRs, whilst lower case indicates the coding region. The start codon (ATG) and stop codon (TAA) are shadowed and in bold, and the consensus polyA signal in the 3ʹUTR is in italic and double-underlined. The three characteristic signatures of the HSP70 family are underlined: the non-organelle consensus-motif (RARFEEL) and the cytoplasmic C-terminal region EEVD are shown. The putative bipartite nuclear localization signal (KK and RRLRT) is shadowed in grey. (B) Phylogenetic tree inferred from nucleotide sequences of hsp70 in different dipteran species. The tree was constructed using Phylogeny.fr tool at ExPASy Proteomics server (http://www.phylogeny.fr) using the “One Click” mode with default settings. The numbers above the branches are tree supported values generated by PhyML using the approximate Likelihood Ratio (aLRT) statistical test. (C) Phylogenetic tree inferred from the inferred amino-acid sequence of HSP70 in different dipteran species. The tree was constructed using Phylogeny.fr tool at ExPASy Proteomics server (http://www.phylogeny.fr) using the “One Click” mode with default settings. The numbers above the branches are tree supported values generated by PhyML using the approximate Likelihood-Ratio (aLRT) statistical test.