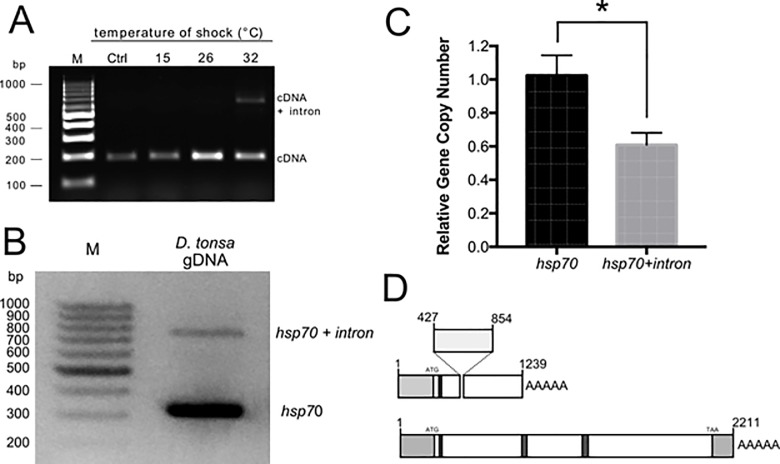
Fig 2. Identification of an Hsp70 pseudogene in Diamesa tonsa.
(A) Agarose gel of hsp70 PCR products from D. tonsa larvae control (Ctrl, 4°C) or maintained for 1 h at 15, 26, and 32°C. All PCR products are amplified from cDNA with primers for hsp70 (Table 1). (B) Agarose gel electrophoresis of the PCR products amplified from D. tonsa genomic DNA with hsp70 sequence specific primers hsp70 F and hsp70 R (Table 2). (C) Relative gene copy number of hsp70 and hsp70 + intron assessed by Real-PCR analysis (n = 4) (Student t-test, * p ≤ 0.05). (D) Schematic representation of the two hsp70 transcripts: light grey boxes are the 5ʹ and 3ʹ UTR, dark grey boxes indicated the position of the three characteristic HSP70 family domains.