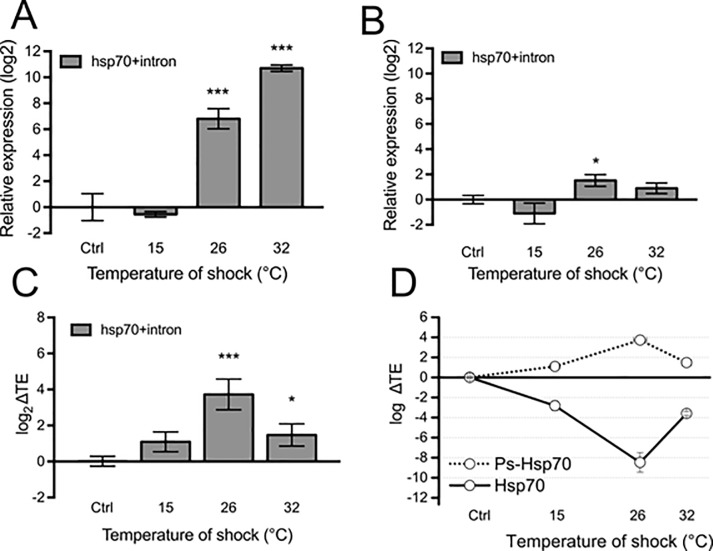
Fig 4. Ps-Hsp70 is loaded on polysomes and acts as a putative ribosome sponge for Hsp70.
(A) Transcriptional expression level for hsp70 + intron mRNA. Total RNA was extracted from Diamesa tonsa larvae control (K, 4°C) or maintained for 1 h at 15, 26, and 32°C. Relative expression level was measured by real-time PCR. Actin was used as housekeeping gene and the level of control (Ctrl, 4°C) was set at 0. Error bars represent SE; n = 3 biological replicates and each assay performed in triplicate. (B) Translational expression level of hsp70 + intron. Polysomal RNA was extracted from sucrose fractions corresponding to the polysomal peaks of larvae control (4°C) or maintained for 1 h at 15, 26, and 32°C. Relative expression level was measured by real-time PCR. Actin was used as housekeeping gene and the level of control (4°C) was set at 0. (C) Translation Efficiency (log2 ΔTE), calculated as the difference between the fold change at the polysomal level and the fold change at the sub-polysomal level, of hsp70 + intron in larvae control (Ctrl, 4°C) or maintained for 1 h at 15, 26, and 32°C. Asterisks indicate statistically significant differences in respect to the control (Student t-test, * p ≤ 0.05, ** p ≤ 0.01, *** p ≤ 0.001). (D) Comparison between the Translation Efficiency (log2 ΔTE) of Ps-Hsp70 and Hsp70. The ΔTE values for Hsp70 were obtained from data shown in Fig 3B and 3C.