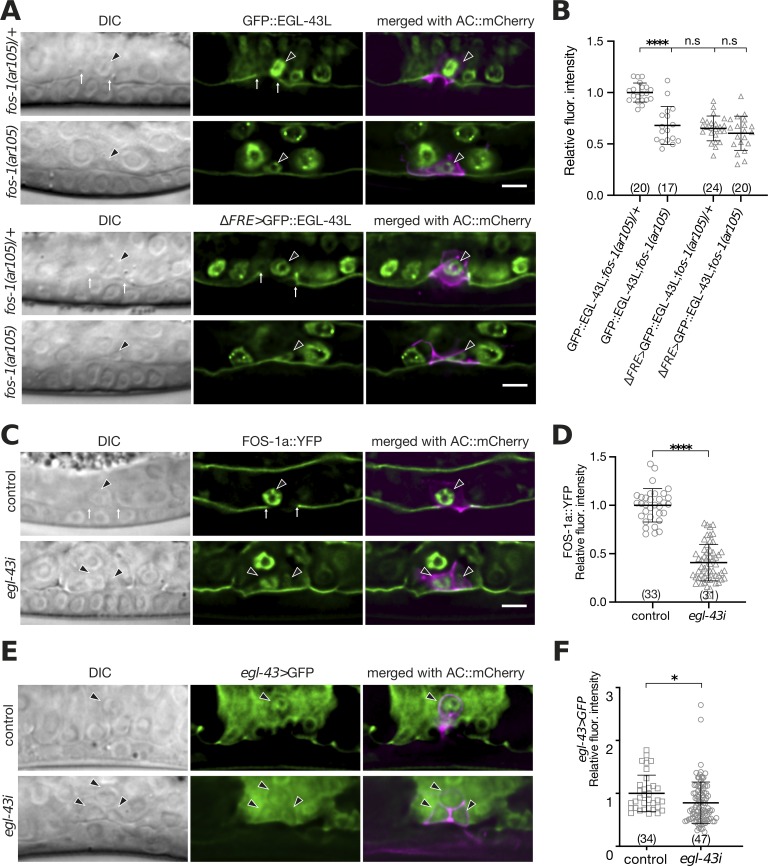
Fig 5. egl-43 and fos-1 regulate each other’s expression.
(A) Expression of endogenous GFP::EGL-43L and of the mutant ΔFRE>GFP::EGL-43L reporter carrying a deletion of the Fos-responsive element TTACTCATCTT (ΔFRE), each in a fos-1(ar105)/+ heterozygous and fos-1(ar105) homozygous background at the mid-L3 stage. (B) Quantification of GFP::EGL-43L expression levels in the ACs of the indicated mutant backgrounds. (C) Expression of a FOS-1a::YFP reporter after control and egl-43 RNAi. (D) Quantification of FOS-1a::YFP levels in the ACs after control RNAi. (E) Expression of a transcriptional egl-43>gfp reporter in the ACs after control and egl-43 RNAi. (F) Quantification of the transcriptional egl-43>gfp reporter expression shown in (E). For each reporter, the left panels show Nomarski (DIC) images, the middle panels the GFP signals of the indicated reporters in green (in (A) and (C) together with the LAM-1::GFP BM marker) and the right panels the GFP reporter signals merged with the ACs labelled with the cdh-3>mCherry::PH reporter in magenta. The black arrowheads point at the AC nuclei and the white arrows at the locations of the BM breaches. The error bars indicate the standard deviation and the horizontal bars the mean values. Statistical significance was determined with a Student’s t-test and is indicated with n.s. for p>0.05, * for p<0.05 and **** for p<0.0001. The numbers in brackets refer to the numbers of animals analyzed. The scale bars are 5 μm.