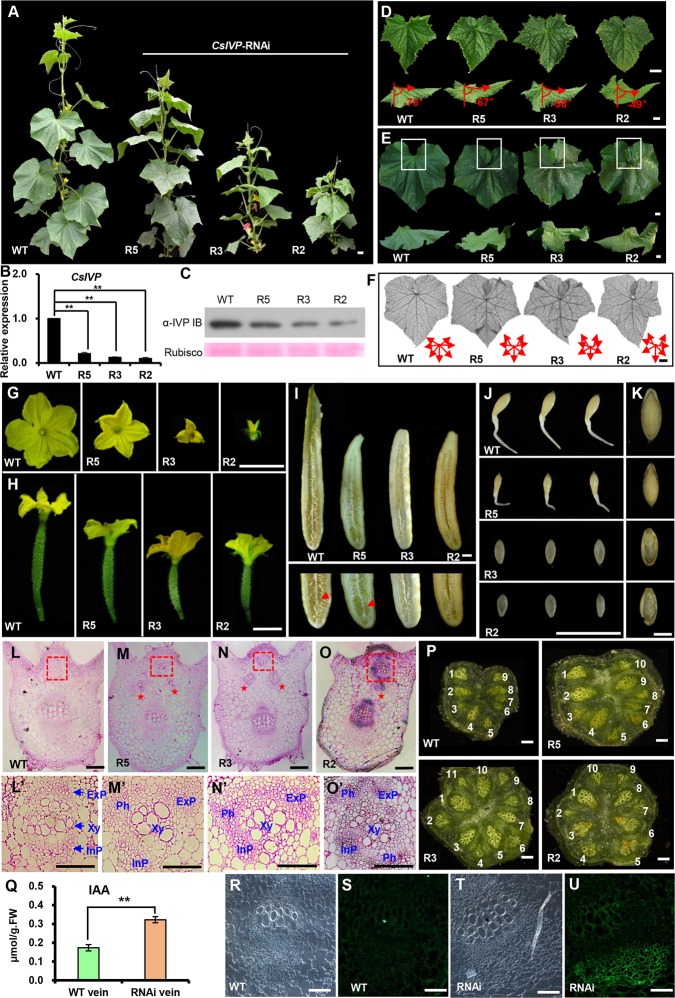
Fig 2. Phenotypic characterization of CsIVP-RNAi transgenic plants.
(A) Plant morphology of WT and CsIVP-RNAi lines R5, R3, and R2. (B) qRT-PCR analysis indicates reduced expression of CsIVP in the CsIVP-RNAi lines. (C) Immunoblot blot analysis indicates reduced CsIVP protein in the CsIVP-RNAi lines. (D–E) Morphology of young (panel D) and mature leaves (panel E) of WT and CsIVP-RNAi lines. White squares represent the gap between the bilateral leaf margins. The angle between the vertical axis and the primary vein indicates the degree of down-curled leaf. (F) Leaf venation in WT and CsIVP-RNAi leaves. Red arrows represent the primary veins in the leaf. (G) Male flower size at anthesis. (H) Fruit at anthesis in WT and CsIVP-RNAi lines. (I) Reduced mature fruit length and decreased seed viability in the CsIVP-RNAi lines. (J) Seeds after 36 h of germination. (K) Seeds after testa removal. (L–O) Transverse sections of leaf mid-veins of WT (panel L) and CsIVP-RNAi (panels M–O) plants. Red stars in panels M–O indicate extra vascular bundles in CsIVP-RNAi lines. (L’–O’) Amplified vascular bundles in red boxes of panels L–O. (P) Transverse sections of stems from WT and CsIVP-RNAi lines. White numbers indicate the vascular bundles. (Q) IAA content in leaf veins of WT and CsIVP-RNAi transgenic plants. (R–U) IAA distribution in leaf veins as detected by immunolocalization. Anti-IAA monoclonal antibodies and DyLight 488–conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG antibodies were used to detect IAA. (R, T) Differential interference contrast images; (S, U) fluorescent images. Scale bars represent 2 cm in panels A, D–J, and P; 2 mm in panel K; 200 μm in panels L–O; 50 μm in panels L’–O’; and 100 μm in panels R–U. Values are means ± SE (n = 3) in panels B and Q. Double asterisks indicate significant difference at P < 0.01 by t test. The data underlying this figure are included in S1 Data. CsIVP, Cucumis sativus Irregular Vasculature Patterning; ExP, external phloem; IAA, indole-3-acetic acid; IgG, immunoglobulin G; InP, internal phloem; Ph, phloem; qRT-PCR, quantitative real-time PCR; RNAi, RNA interference; WT, wild type; Xy, xylem.