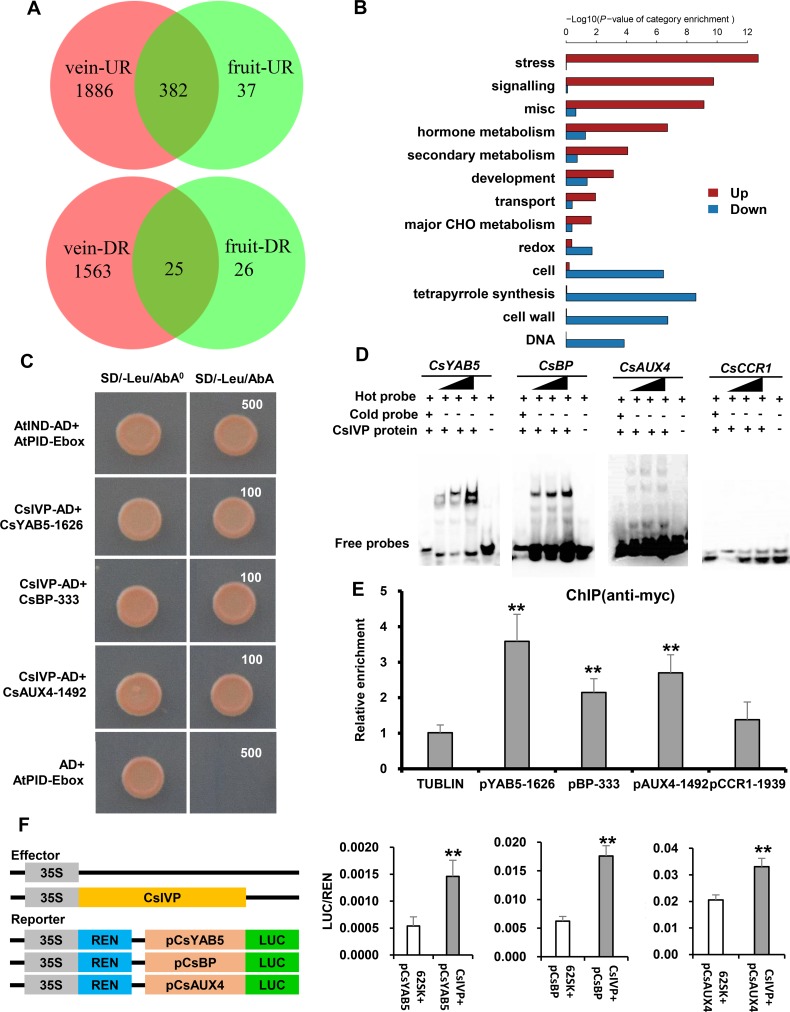
Fig 3. Transcriptome and interaction analysis between CsIVP and putative downstream vascular-related targets.
(A) Venn diagrams of the overlapping DEGs that were up-regulated or down regulated in the vein and fruit of CsIVP-RNAi plants, as compared to WT plants. (B) Gene category enrichment of up- and down-regulated genes in the vein of CsIVP transgenic compared to WT plants. (C) Yeast one-hybrid assays identify interactions between CsIVP and the E-box from the CsYAB5, CsBP, and CsAUX4 promoters. Activation of AbAr occurred when CsIVP bound to the E-box sequence. The SD/-Leu medium with 100 ng/ml or 500 ng/ml inhibitory AbA was used to screen for interactions. (D) Visualization of direct binding of CsIVP to promoters of CsYAB5, CsBP, CsAUX4, and CsCCR1 via EMSAs. Three concentrations of labeled probe were used (80, 120, and 160 fmol). Cold (unlabeled) probes were used as competitors. (E) ChIP-PCR showing the in vivo binding of CsIVP to the pCsYAB-1626, pCsBP-333, and pCsAUX4-1492 promoters. The cucumber alpha-tubulin gene (CsTUBULIN, GenBank: AJ715498) was used as the internal gene control, the pCsCCR1-1939 was used as a negative amplification. Values are means ± SE (n = 3). Double asterisks indicate significant difference at P < 0.01 by t test. (F) Luciferase activity measured in tobacco leaves after co-expression of 35S:CsIVP with proCsYAB5:LUC, or proCsBP:LUC, or proCsAUX4:LUC. Values are means ± SE (n = 6). Double asterisks indicate significant difference at P < 0.01 by t test. The data underlying this figure are included in S2 Data. AbA, aureobasidin A; AbAr, AbA resistance gene; AUX4, AUXIN/INDOLEACETIC ACIDS4; BP, BREVIPEDICELLUS; CCR1, CINNAMOYL COA REDUCTASE1; ChIP, chromatin immunoprecipitation; Cs, Cucumis sativus; CsIVP, Cucumis sativus Irregular Vasculature Patterning; DR, down-regulated; EMSA, electrophoretic mobility-shift assay; RNAi, RNA interference; SD/-Leu, synthetical dropout/-leucine; UR, up-regulated; WT, wild type; YAB5, YABBY5.