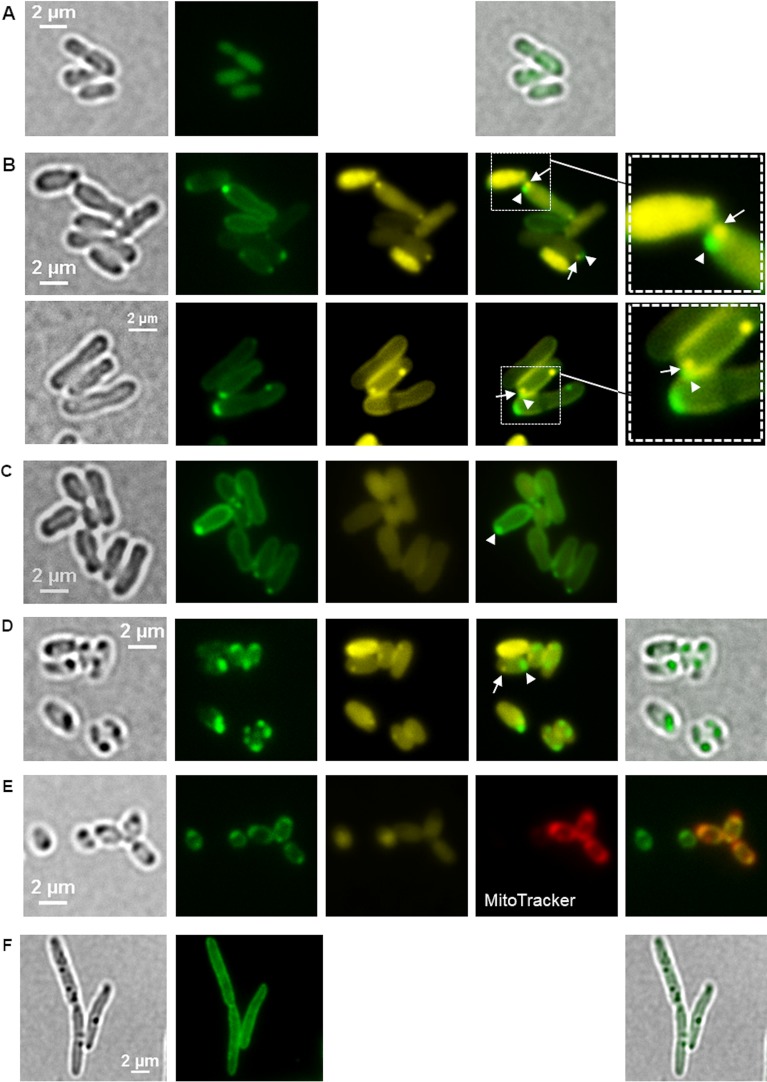
FIG 5.
Localization of eYFP-HppA in A. tumefaciens. (A) Homogeneous fluorescence in cells expressing eyfp without fusion confirmed that eYFP is a soluble, cytoplasmic protein in A. tumefaciens. Samples were taken from three biological replicates. (B) A. tumefaciens cells harboring pBBR1MCS2-PphaC-eyfp-hppA were stained with DAPI and imaged (from left to right) by bright field and fluorescence microscopy using an eYFP-specific filter and a DAPI-polyP-specific filter. The image second from the right shows an overlay of the eYFP channel and the DAPI-polyP channel with a magnification shown in the rightmost image. Arrowheads and arrows point to eYFP-HppA foci and DAPI-polyP foci, respectively, located side by side at the cell pole. Microscopy images were taken from four biological replicates. (C) polyP-free mutant of A. tumefaciens (Δppk1 Δppk2 mutant) harboring pBBR1MCS2-PphaC-eyfp-hppA. The experiment was performed in two biological replicates. (D) LB-grown cells of A. tumefaciens (48 h) with a genomic eyfp-hppA integration. (E) eYFP-HppA foci were strongly visible, and additional staining with MitoTracker showed a colocalization of the MitoTracker and eYFP-HppA signals. (F) Introduction of the pBBR1MCS2-PphaC-eyfp-hppA plasmid into R. eutropha resulted in only membrane staining and no formation of fluorescent foci. Samples were analyzed in three (D and E) and two (F) biological replicates.