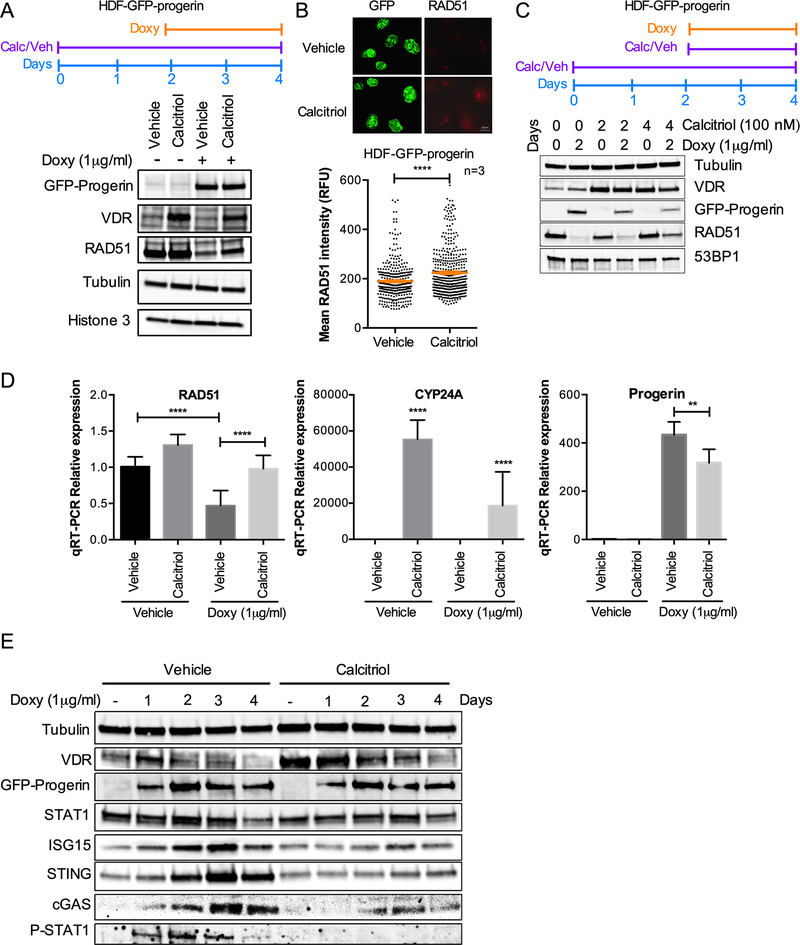
Figure 4. Calcitriol prevents RAD51 loss and cGAS/STING/IFN activation caused by progerin.
(A) HDF-GFP-progerin cells were treated with calcitriol (100nM 1α,25-dihydroxy-vitamin D3) for 2 days prior to induction of GFP-progerin by Doxy. The levels of VDR and RAD51 under the different conditions are shown. Note how the decrease in RAD51 upon progerin expression is partly rescued by calcitriol. β-tubulin and histone H3 used as loading control. (B) Immunofluorescence in HDF-GFP-progerin cells treated with calcitriol or vehicle 2 days prior to Doxy induction of GFP-progerin for 4 days. Graph shows quantitation of RAD51 labeling intensity (relative fluorescence units), as measured by ImageJ program. GFP staining was used to demarcate nuclei. Results are the average ± s.e.m. of 3 independent experiments. (C) HDF-GFP-progerin cells were pre-treated with calcitriol (100 nM) for 2 days prior to induction of GFP-progerin by Doxy or treated with both calcitriol and Doxy at the same time. The levels of VDR and RAD51 under the different conditions are shown. Note how the pre-treatment with calcitriol is necessary to partially prevent RAD51 loss upon progerin expression. β-tubulin used as loading control. 53BP1 levels are also constant in the different conditions. (D) Relative expression of RAD51, CYP24A, and progerin-specific transcripts by qRT-PCR in HDF-GFP-Progerin cells pretreated with calcitriol or vehicle for 2 days followed by Doxy or vehicle for 4 days. Results are average ± s.e.m. of 2 biological repeats, each performed in triplicate. (E) HDF-GFP-Progerin cells were pretreated with calcitriol or vehicle for 2 days, followed by Doxy for increasing days. Activation of cGAS/STING/IFN pathway monitored by immunoblotting. β-tubulin is the loading control. VDR shows the effect of calcitriol. Note the robust effect of calcitriol preventing the upregulation of cGAS, STING, STAT1, P-STAT1 and ISG15.