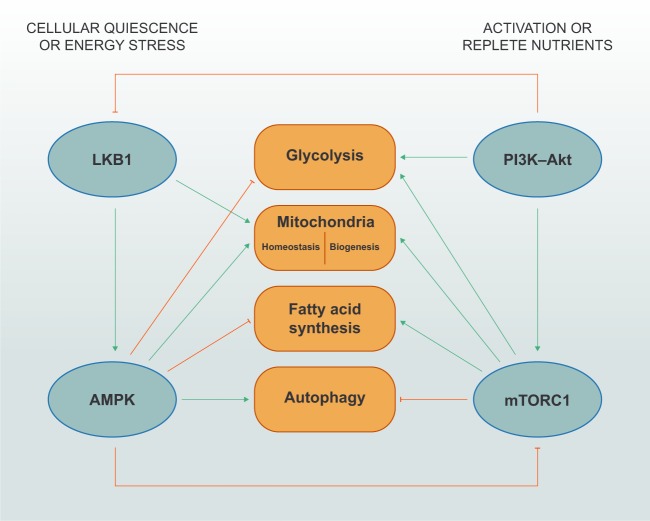
Fig. 4. Cross-regulation of immunometabolic signaling pathways.
Under nutrient-deprived conditions, LKB1–AMPK signaling inhibits anabolism-associated programs, such as glycolysis and fatty acid synthesis, while promoting mitochondrial homeostasis and autophagy; however, these mechanisms require additional investigation in primary T cells. AMPK directly inhibits mTORC1 through phosphorylation of its obligate adapter protein Raptor (not depicted). During activation and/or replete nutrient conditions, PI3K–Akt and mTORC1 signaling promotes glycolysis, mitochondrial biogenesis and fatty acid synthesis, while inhibiting autophagy. Akt can reportedly phosphorylate LKB1 to suppress its functional localization, but this regulation is not yet reported to occur in T cells.