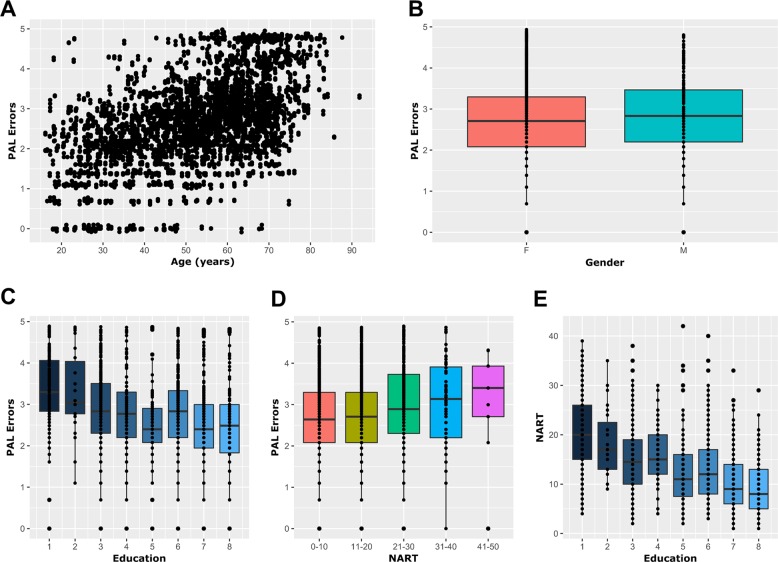
Fig. 4. Epidemiological analysis in TwinsUK cohort shows age, NART errors and education level are predictive of cognitive performance.
a Scatter plot showing the significant correlation between age and PAL errors suggesting increasing age is associated to a decline in performance. b Tukey boxplot showing the non-significant association between gender and PAL error (Welch’s t test). c–e Tukey boxplot showing the significant correlations between education measure and age (c), National Adult Reading Scale (NART) and age (d) and NART errors and education measure (e). These results show that education level measured either via attained qualification or NART performance is an important co-variate when assessing cognitive performance. For (c–e), data were treated as continuous but graphed as categorical for ease of visualisation. Each dot represents a participant.