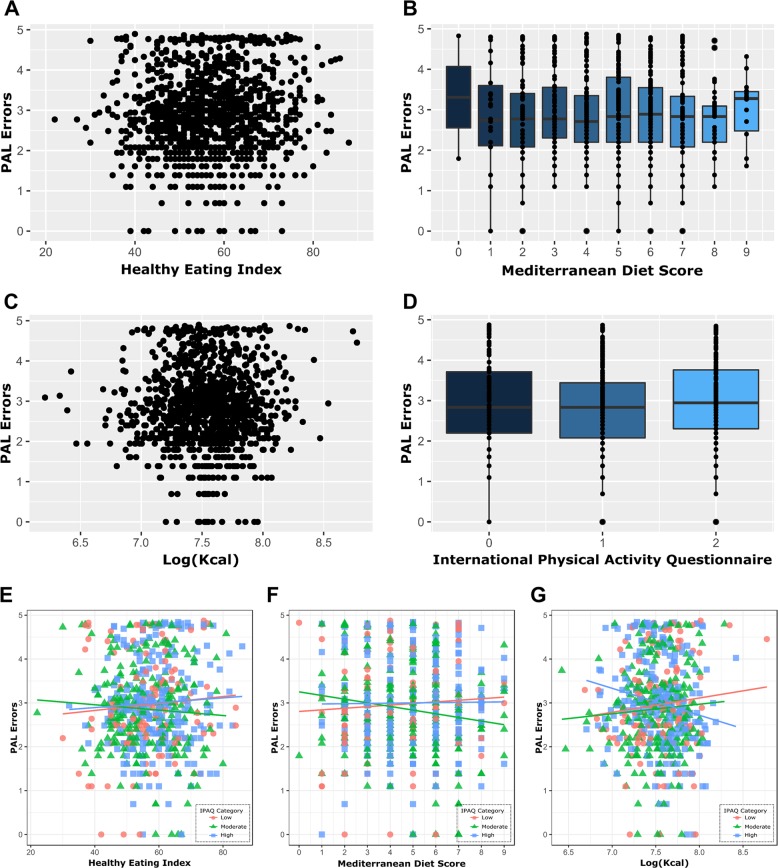
Fig. 5. Physical activity modulates the association between calorie intake and PAL performance in the TwinsUK cohort.
Individual lifestyle measures showed no association to PAL errors as shown in graphs (a–d). Scatter plots showing the lack of association between PAL errors and healthy eating (a) and between PAL errors and calorie intake (c). Tukey boxplots showing the lack of association between PAL errors and adherence to Mediterranean diet (b) and between PAL errors and physical activity (d). e–g Scatterplots showing the interaction between physical activity and diet testing whether lifestyle measures can interact and thereby affect each other’s association to PAL errors. Physical activity had no effect on the association between healthy eating and PAL errors (e) or on the association between adherence to Mediterranean diet and PAL errors (f). Physical activity, however, significantly affected the association between Kcal intake on PAL errors (g) showing that calorie intake and cognitive performance can have either a positive or negative association depending on the individual’s physical activity level.