Fig. 1.
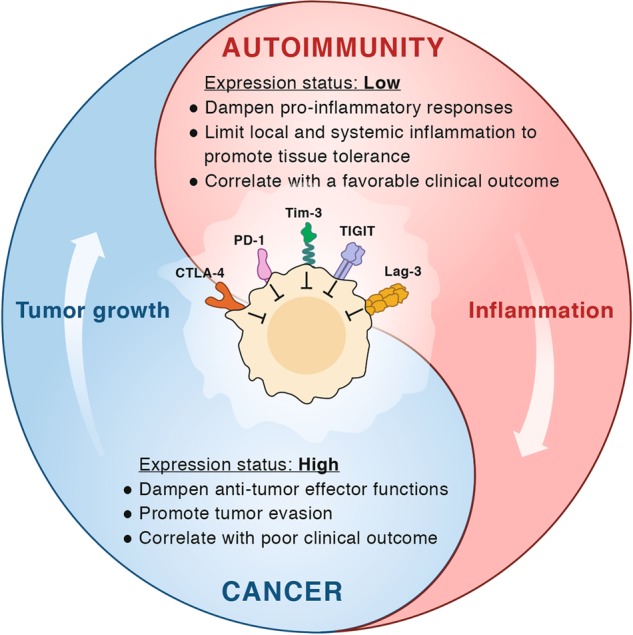
The Yin and Yang of co-inhibitory receptors. Schematic representation of the co-inhibitory receptors’ functional role in autoimmunity and cancer. In the tumor, co-inhibitory receptors on T cells dampen T-cell effector functions thereby enhancing tumor progression and correlating with worse clinical outcome. In autoimmunity, these receptors play a role in reducing local and systemic tissue inflammation, maintaining tissue tolerance, and their increased expression is associated with a good clinical outcome
