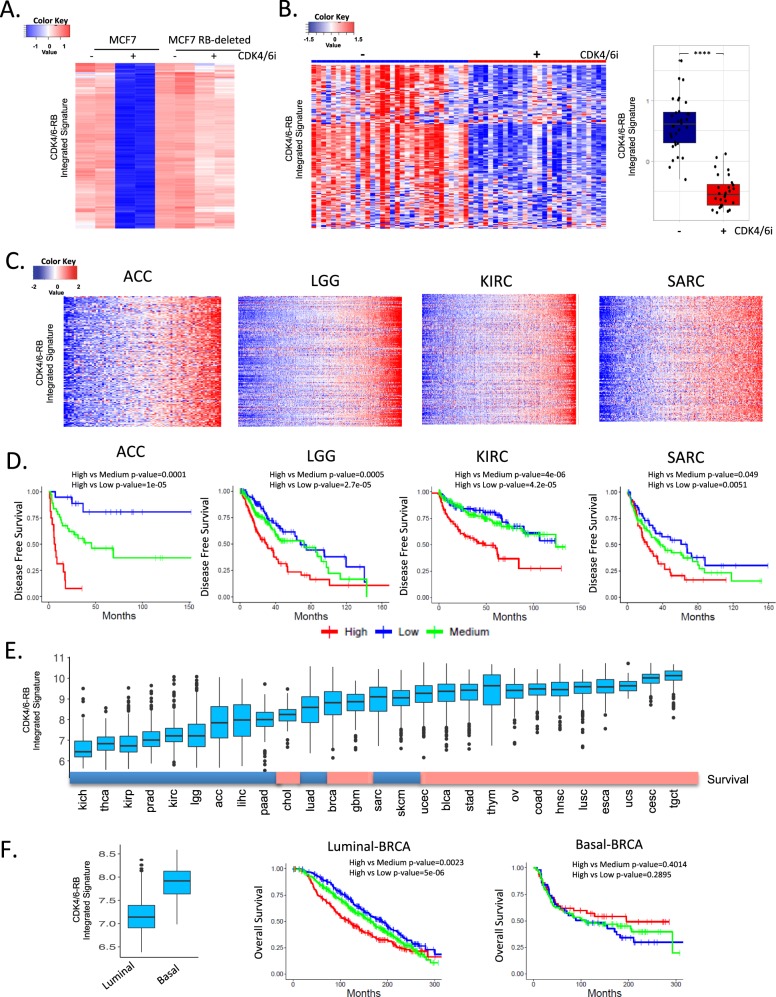
Fig. 3. CDK4/6-RB integrated signature and prognosis.
a MCF7 cells and isogenic RB1 deleted model were treated with CDK4/6 inhibitor (250 nM palbociclib) for 48 h. RNA sequencing was used to define transcriptional repression events that are RB dependent thereby linking CDK4/6 inhibition to RB-activation. b The CDK4/6-RB integrated signature was applied to data from the NeoPalaAnna trial and exhibited consistent repression in this clinical cohort of tumors treated with CDK4/6 inhibitors (pre-treatment N = 32, on treatment N = 28). Box plot shows difference in the integrated signature between pre and on-treatment samples (Student’s t-test two sided: ****p < 0.0001) c Heatmaps illustrate that general behavior of the CDK4/6-RB integrated signature across several tumors types. d Kaplan–Meier analysis of the indicated tumor types stratified by CDK4/6-RB integrated signature. Disease-free survival is shown, and statistical analysis is by log-rank approach. e Pan-cancer relationship of the CDK4/6-RB integrated signature expression value. Color bar indicates tumors wherein high levels of the CDK4/6-RB integrated signature (indicative of high CDK4/6 activity or RB loss) are significantly associated with poor prognosis (blue) or not (red). f Relative expression of the CDK4/6-RB integrated signature in luminal (N = 1175) vs. basal (N = 209) breast cancer subtypes in the METABRIC data set (Student’s t-test two side: p < 0.001). Kaplan–Meier analysis of luminal and basal breast cancer stratified by the CDK4/6-RB integrated signature. Statistical analysis is by log-rank approach.