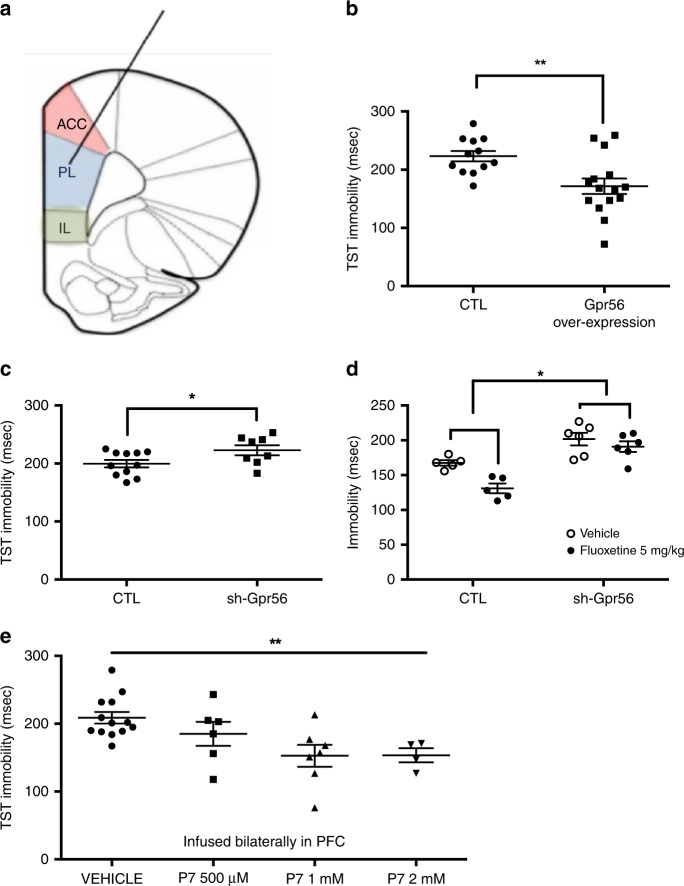
Fig. 3. Gpr56 regulates depressive-like behaviors.
a Mice were injected bilaterally in the pre-frontal cortex with control (CTL) or lentivirus-Gpr56 constructs, as well as with CTL or lentivirus-sh-Gpr56 (inhibitor) constructs. b Overexpression of Gpr56 (n = 15) was associated with lower immobility time in the TST in comparison to control animals (n = 12), two-sided t = 3.07, p = 0.005. c Downregulation of Gpr56 (n = 8) produced increased immobility time, i.e. depressive-like behavior in the tail suspension test (TST) in comparison to control animals (n = 11), two-sided t = 2.203, p = 0.048. d Fluoxetine decreased immobility in control animals (n = 5), while this effect was strongly attenuated in sh-Gpr56-virus infused animals (n = 6); two-way ANOVA for repeated measures; treatment × group interaction F(1,9) = 6.80, p = 0.028; main effects for group F (1,9) = 25.4, p = 0.001 (as compared to control) and for treatment F(1,9) = 6.80 p = 0.001 (as compared to vehicle). e GPR56 agonist P7 has antidepressant-like effects. GPR56 agonist P7 peptide infused bilaterally with escalating doses in PFC decreases immobility time and demonstrates antidepressant-like effects, ANOVA F(1,4) = 4.88 p = 0.008. In comparison to vehicle (n = 13), both 1 mM (n = 7) and 2 mM (n = 4) doses demonstrate a significant decrease of immobility time (p < 0.01 and p = 0.01 respectively, two-sided post hoc test). Bars represent mean. Error bars represent standard error of the mean. **p < 0.01, *p < 0.05. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.