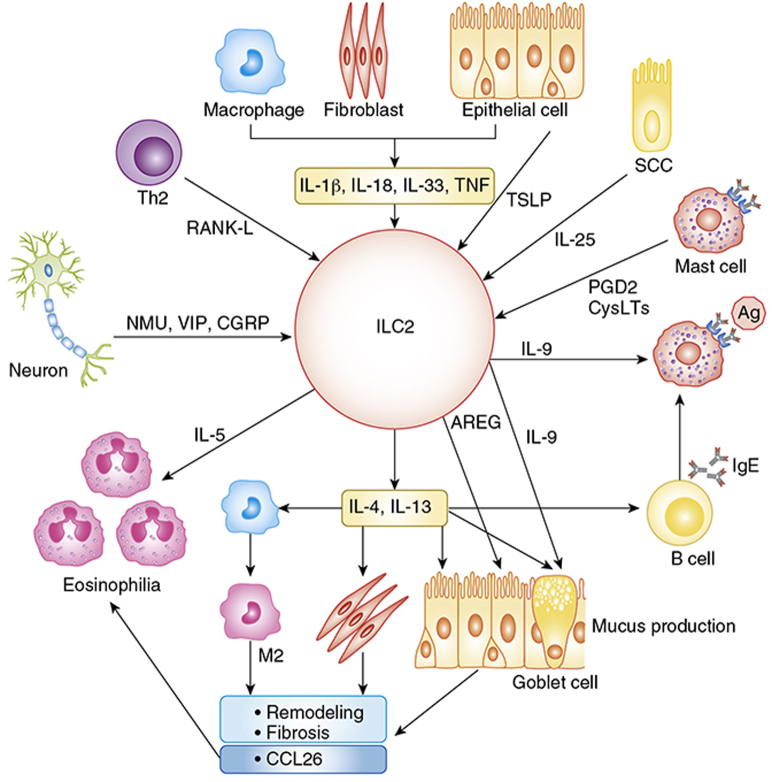
Figure 1.
Group 2 innate lymphoid cell (ILC2s) contribute to airway inflammation via the production of type 2 cytokines and amphiregulin. ILC2s produce type 2 cytokines in response to stimulation with several cytokines such as TNF and IL-1 family cytokines from epithelial cells, fibroblasts, and macrophages; TSLP from epithelial cells; IL-25 from SCCs and RANK-L from Th2 cells; lipid mediators from mast cells; and neuropeptides from neurons. IL-5 promotes eosinophilia and IL-9 induces goblet cell metaplasia and mast cell growth. AREG controls fibrosis and remodeling in epithelial cells. IL-4 and IL-13 activate macrophages, B cells, fibroblasts, epithelial cells, and goblet cells to induce eosinophil recruitment, mucus production, remodeling, fibrosis, and IgE-mediated reactions. Ag = antigen; AREG = amphiregulin; CGRP = calcitonin gene-related peptide; CysLTs = cysteinyl leukotrienes; M2 = M2 macrophage; NMU = neuromedin U; PGD2 = prostaglandin D2; RANK-L = receptor activator of NF-κB ligand; SCC = solitary chemosensory cell; Th2 = helper T type 2; TNF = tumor necrosis factor; TSLP = thymic stromal lymphopoietin; VIP = vasoactive intestinal peptide.