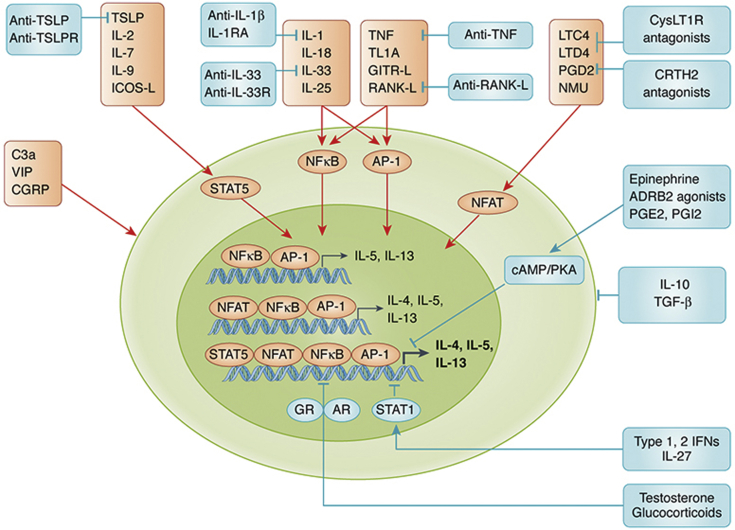
Figure 2.
Schematic of activation and inhibition pathways for ILC2s. IL-1 family cytokines, IL-25, and TNFSFs weakly induce IL-5 and IL-13 via activation of NF-κB and AP-1. Activation of NFAT by lipid mediators and NMU is required for induction of IL-4. IL-2 and IL-7 family cytokines and ICOS-L act as costimulators and potently enhance cytokine- and lipid mediator-mediated induction of IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 via the activation of STAT5 in ILC2s. Although C3a, VIP, and CGRP activate ILC2s, at least in mice, their signaling pathways in ILC2s have not been elucidated. Testosterone and glucocorticoids suppress NF-κB-mediated induction of type 2 cytokines via activation of nuclear receptors, AR and GR, respectively. IFN- and IL-27-mediated inhibition of ILC2s occurs via the STAT1 pathway. The activation of cAMP and PKA is involved in ADRB2 agonist-, PGE2-, and PGI2-mediated inhibition. IL-10 and TGF-β also suppress functions of ILC2s. Furthermore, monoclonal antibodies and receptor antagonists against activation pathways of ILC2s are commercially available or in clinical trials. ADRB2 = β2-adrenergic receptor; AR = androgen receptor; cAMP = cyclic AMP; CRTH2 = chemoattractant receptor-homologous molecule expressed on Th2 cells; CysLT1R = cysteinyl leukotriene receptor 1; GITR-L = glucocorticoid-induced TNFR-related protein ligand; GR = glucocorticoid receptor; ICOS-L = inducible T-cell costimulatory ligand; IFN = interferon; IL-1RA = IL-1 receptor antagonist; IL-33R = IL-33 receptor; LTC4, LTD2 = leukotrienes C4 and D2; NF-κB = nuclear factor-κB; NFAT = nuclear factor of activated T cells; PGD2, PGE2, PGI2 = prostaglandins D2, E2, and I2; PKA = protein kinase A; STAT1, STAT5 = signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 and 5; TL1A = TNF-like cytokine 1A; TNFSF = TNF superfamily; TSLPR = thymic stromal lymphopoietin receptor. See Figure 1 legend for expansion of other abbreviations.