Figure 2.
miR-21 Targets and Pathways Associated with the Hallmarks of Cancer
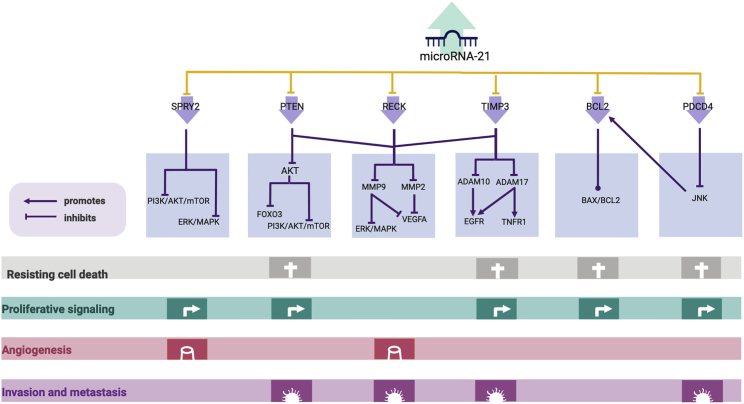
The upregulation of miR-21 can lead to the downregulation of target genes involved in the carcinogenic process, such as SPRY2,146 PTEN,97 RECK,147 TIMP3,64 BCL2,115 and PDCD4.84 In addition, SPRY2 can negatively regulate the PI3K/AKT/mTOR and ERK/MAPK pathways by controlling the trafficking of EGFR and HER2 through the endosome and by inhibiting Raf1, respectively.148 Therefore, in its absence, uncontrolled proliferation is observed, but angiogenesis is suppressed.149 PTEN, another miR-21 target, can also control the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway by inhibiting AKT activation. In this case, AKT can inhibit FOXO3, which regulates cell survival, growth, and differentiation by inducing the expression of proapoptotic BCL2 family proteins and Fas and TRAIL ligands or by enhancing cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors (CDKIs).150,151 Additionally, AKT can activate mTORC1 by the phosphorylation and inactivation of TSC2 or by the phosphorylation of PRAS40,152 which affects cell growth, proliferation, survival, and motility.153 Alternatively, RECK can negatively control two matrix metallopeptidases, MMP-2 and MMP-9, which inhibit angiogenesis and invasion.154,155 In addition, TIMP3 negatively regulates ADAM10 and ADAM17, two metalloproteinases that are upregulated in cancer, and receptor substrates such as Notch receptors, transforming growth factor β (TGF-β), HER2, HER4, and VEGFR2, among others.156 In contrast, BCL2 expression can be induced by miR-21 binding to its 3′ UTR, which decreases apoptosis and increases proliferation115 by dysregulating the BAX/BCL2 ratio.157 Finally, PDCD4, a miR-21 target, can interfere with JNK activation and lead to the upregulation of BLC2-like proteins and affect apoptosis, proliferation, and migration.158