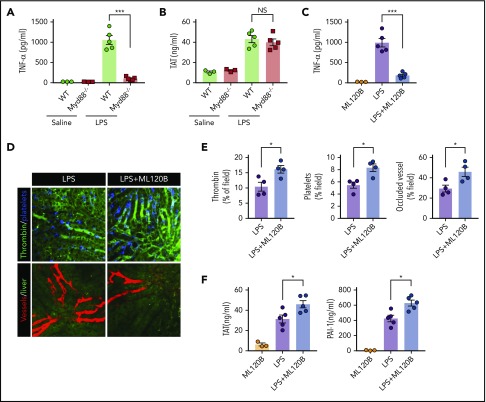
Figure 3.
Inhibition of NF-kB activation enhanced LPS-induced coagulation. (A) Plasma concentration of TNF-α was measured at 1 hour after Myd88-deficient and WT mice were injected with 0.4 mg/kg of LPS. (B) Plasma concentration of TAT was measured in Myd88-deficient and WT mice primed with 0.4 mg/kg of LPS and then challenged with 10 mg/kg of LPS for 8 hours. (C-F) WT mice were treated with or without the IKKβ inhibitor ML120B (400 mg/kg by oral gavage twice daily for 4 days). Plasma concentration of TNF-α was measured at 1 hour after 0.4 mg/kg of LPS was injected into mice pretreated with or without ML120B (C). Representative SD-IVM images of thrombin (green), platelet adhesion (blue), and albumin (red) within the liver microvasculature in mice pretreated with or without ML120B, and then challenged with 4 mg/kg of LPS for 6 hours (D). Quantitative analysis of thrombin, platelets, and occluded vessels within the liver microcirculation by using ImageJ software (E). Plasma concentration of TAT complexes and PAI-1 were detected in mice pretreated with or without ML120B, and primed with 0.4 mg/kg of LPS for 7 hours followed by10 mg/kg of LPS for 8 hours (F). *P < .05; ***P < .001. NS, not significant.