Fig. 2.
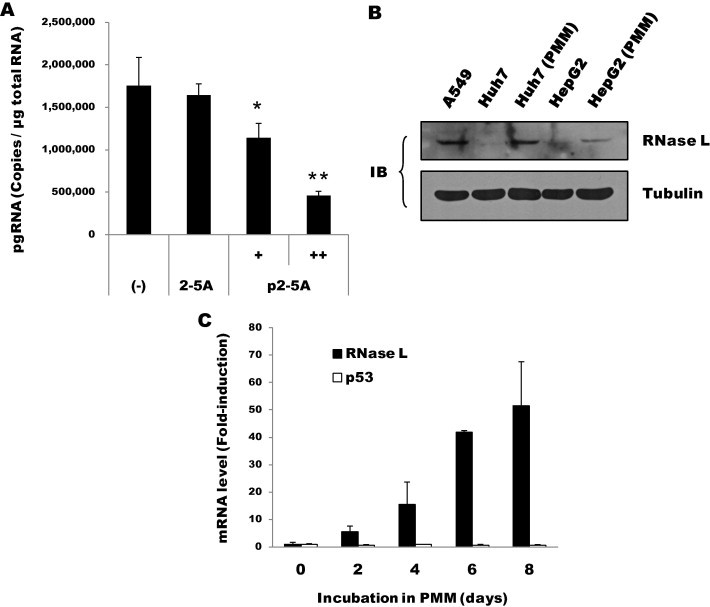
Antiviral activity and expression of RNase L. (A) Antiviral activity mediated by p2–5A. At 16 h after infection, HepG2-NTCP cells were mock-transfected (–) or transfected with 2–5A (100 μM) or p2–5A (30 and 100 μM). Intracellular pgRNA at 9 days post-infection was measured by RT-qPCR (∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01). (B) Aliquots of Huh-7 or HepG2 cells either grown in DMEM or further incubated in PMM for 5 days were immunoblotted for RNase L (∼82 kDa). Human lung carcinoma (A549) cells grown in DMEM were also probed. Tubulin served as a loading control. (C) RNase L mRNA levels in HepG2 cells incubated in PMM for the indicated periods were measured by RT-qPCR and are shown as fold-induction relative to the initial level. For comparative purposes, p53 mRNA is also shown.
