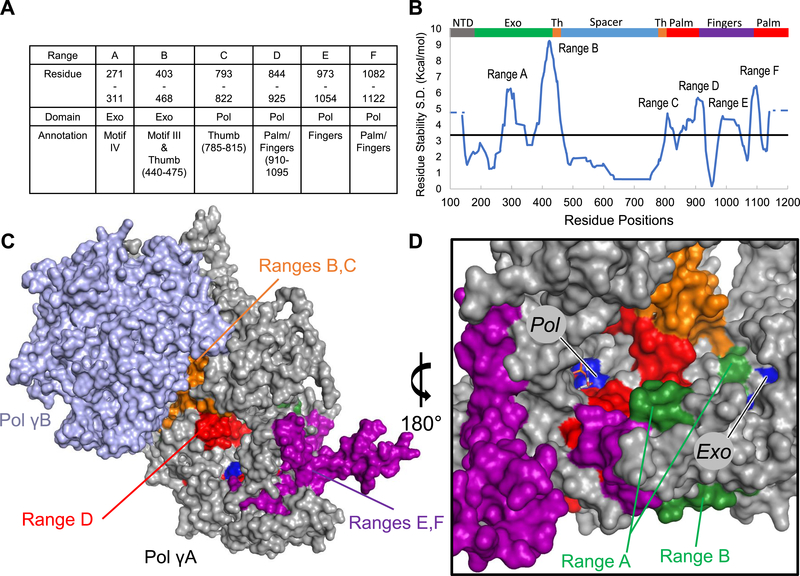
Figure 2.
Different dNTP/NRTI perturb local and nonlocal regions of Pol γ. (A) The hypervariable regions are shown in the table along with their domain, subdomain, and motif associations.20,21 (B) Population standard deviation (S.D.) of residue stability for each complex is plotted as the regional average of 30 amino acids, and the horizontal line is the average SD. The N and C termini were not considered hypervariable and so are shown instead as dotted lines. Gray is the N-terminal domain (1–170), green the 3′−5′ exonuclease (170–440), orange the thumb subdomain (440–475 and 785–815), blue the spacer (475–815), red the palm (815–910 and 1095–1239), and purple is the fingers subdomain (910–1095) of pol. (C,D) Ranges A–F are mapped onto the ternary structure (PDB: 4ZTZ) and colored based upon domain assignment (DNA not shown), Pol γA is shown in gray, and Pol γB subunits are shown in light blue. The perturbed thumb domain interacts with Pol γB subunit, which may affect enzyme processivity. (D) Most perturbed residues lie between the two active sites. Active site residues are colored in blue and labeled according to their respective active site, while the dCTP substrate is shown as sticks.