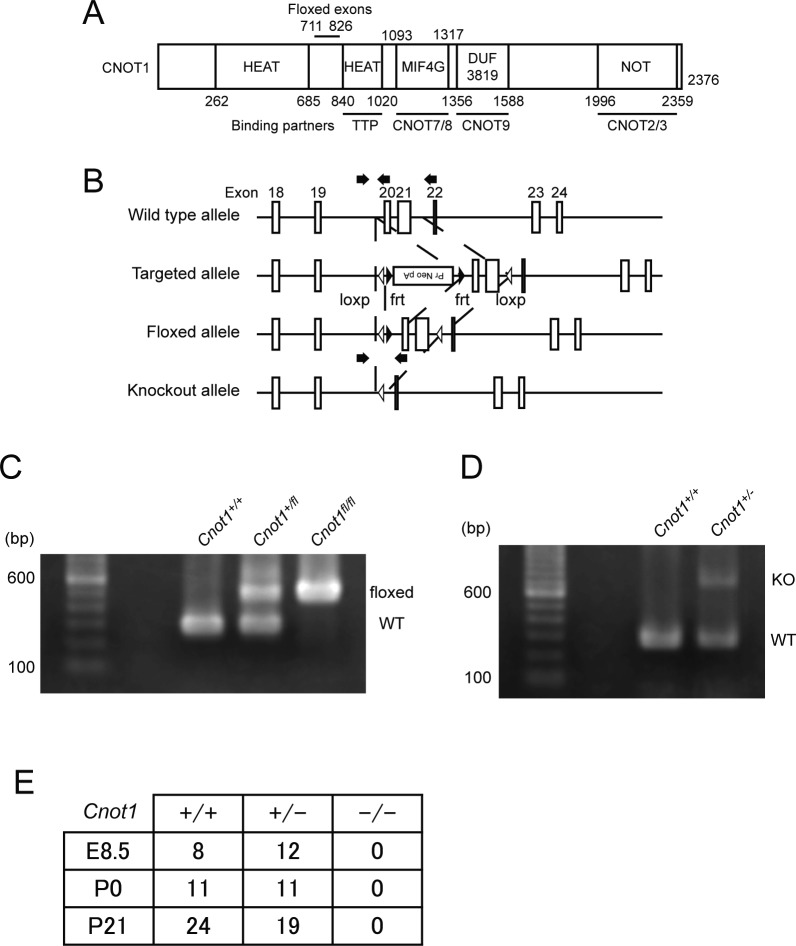
Figure S1. Generation of Cnot1 conditional and KO mice and embryonic lethality of Cnot1-null mice.
(A) Schematic representation of CNOT1 structure. HEAT and NOT represent HEAT repeat and NOT superfamily homology domain. MIF4G and DUF indicate the middle domain of eukaryotic initiation factor 4G and a domain of unknown function, respectively. Binding regions of known interacting molecules are shown at the bottom. (B) Schematic representation of wild-type, targeted, floxed, and KO alleles. Exons 18–24 (white boxes), loxp sequences (white triangles), frt sequences (black triangles), and the neomycin resistance cassette are shown. Arrows indicate positions of PCR primers for genotyping. (C, D) Genotyping PCR analysis using genomic DNA from mouse tails. The leftmost lane contains molecular weight standards. (B, C, D) Wild-type (WT) and floxed (C), and WT and KO alleles (D) were amplified using specific PCR primer sets indicated in (B). Sizes of amplified products for wild-type, floxed, and KO alleles are 279, 732, and 492 bp, respectively. (E) Cnot1-null mice die in early embryonic development. The table shows the number of embryos and pups with the indicated genotypes obtained from mating of Cnot1-heterozygous pairs.