Fig. 1.
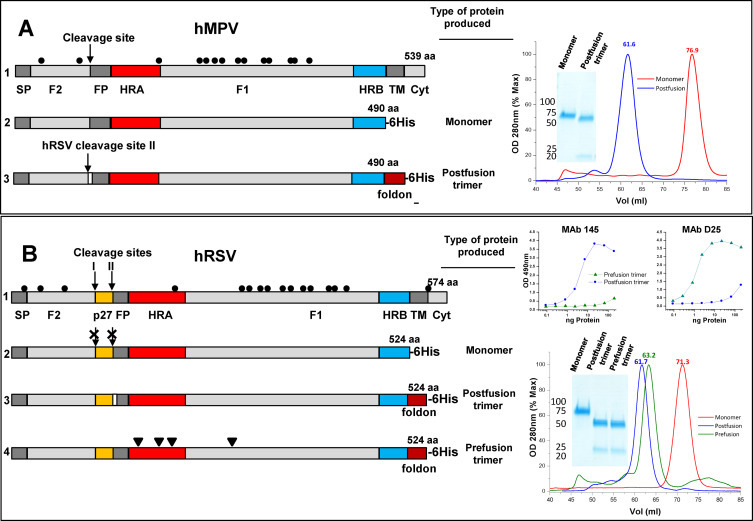
F proteins used in this study: Diagrams of the hMPV_F and hRSV_F primary structures are shown in line 1 of panels A and B, respectively. The signal peptide (SP), F2 subunit, cleavage sites, fusion peptide (FP), F1 subunit, heptad repeats A (HRA) and B (HRB), transmembrane region (TM), and cytoplasmic tail (Cyt) are denoted, as well as the 27 amino acid peptide (p27), unique to hRSV_F. Cysteines are represented by dots. All other lines of panels A and B show the soluble proteins that were produced and purified as described in Section 2, indicating only the structural features that are not represented in the corresponding full-length polypeptide. Panel (A) hMPV_F of line 2 was generated by introducing a 6-His tag after aa 490 to express a monomeric form of the F protein ectodomain. The hMPV_F of line 3 was produced as a soluble post-fusion F protein trimer by adding the foldon trimerization domain at the C-terminus of the protein ectodomain, replacing the hMPV cleavage site by the polybasic cleavage site II of hRSV_F and deleting the first eight amino acids of the fusion peptide (white rectangle). Panel (B) Line 2 shows the hRSV_F ectodomain, expressed as an uncleaved monomer by changing all basic residues of the furin cleavage sites to Ans. The hRSV_F of line 3 is produced as a soluble postfusion trimer (with the first eight FP amino acids deleted) and that of line 4 as a prefusion trimer, stabilized with the mutations (arrowheads) described by McLellan et al. to stabilize their DS-Cav1 variant (McLellan et al., 2013a). Gel filtration profiles and Coomassie stained SDS-PAGE gels of the purified proteins are shown in the right hand of panels A and B. The upper right hand part of panel B shows sandwich ELISAs of the indicated proteins with MAbs specific for either the postfusion (R145, Palomo et al., 2014) or prefusion (D25, McLellan et al., 2013b) conformations of hRSV_F.
