Fig. 4.
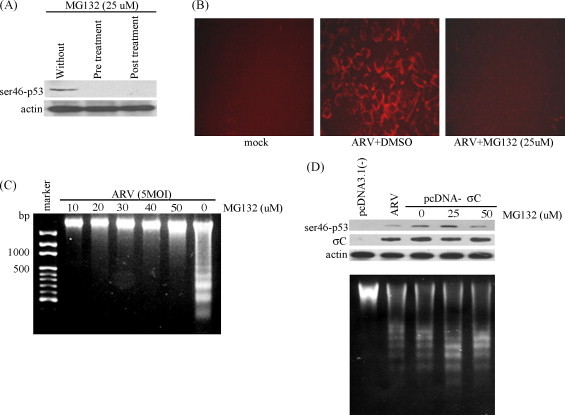
Inhibition of ARV σC-induced apoptosis by a protease inhibitor MG132. (A) BHK-21 cells were either pre-incubated 30 min before infection or 2 h.p.i. with MG132. Cell lysates collected from infected cells 18 h after treatment were assayed by Western blot assay for the presence of ser46-phosphorylated p53 protein expression in ARV-infected BHK-21 cells. (B) Activated caspase 3 staining of ARV-infected BHK-21 cells was carried out to examine inhibition of ARV-induced apoptosis by MG132. Mock and ARV-infected BHK-21 cells treated with or without MG132 were stained18 h.p.i. (C) BHK-21 cells were pre-incubated 30 min before infection with MG132. Cell lysates were collected from infected cells 18 h after treatment with various concentrations of MG132 and assayed by DNA fragmentation analysis. (D) BHK-21 cells were transfected with construct pcDNA-σC and then cells were treated with various concentrations of MG132. Cell lysates were collected 18 h after transfection and assayed by Western blot assay for the presence of ser46-phosphorylated p53 and σC protein expression (upper panel). DNA fragmentation assay was performed to check whether apoptosis was also induced in mock-treated, ARV-infected, and MG132-treated cells (lower panel). Actin, mock-transfection with pcDNA3.1 (−) and ARV-infected cells were used controls, respectively.
